To supply cross-protection towards various influenza virus variants, nanoparticle vaccines can produce pivotal mobile and mucosal immune responses that improve vaccine efficacy and broaden safety, in response to a examine by researchers within the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State College.
The examine, printed within the journal Nature Communications, affords beneficial insights into tailoring immunization methods to optimize influenza vaccine effectiveness. To alleviate the numerous public well being burden of influenza epidemics and occasional pandemics, it is important to reinforce influenza vaccine cross-protection, in response to the authors.
Whereas the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention (CDC) recommends annual influenza vaccination, present seasonal influenza vaccines sometimes present strain-specific and short-lived immunity. Seasonal influenza vaccines supply restricted cross-protection towards antigenically various virus variants and supply no protection towards sporadic influenza pandemics, the authors defined.
“Developing effective influenza vaccines or vaccination strategies that can confer cross-protection against variant influenza viruses is a high priority to mitigate the public health consequences of influenza,” stated Dr. Chunhong Dong, first writer of the examine and a postdoctoral fellow within the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State.
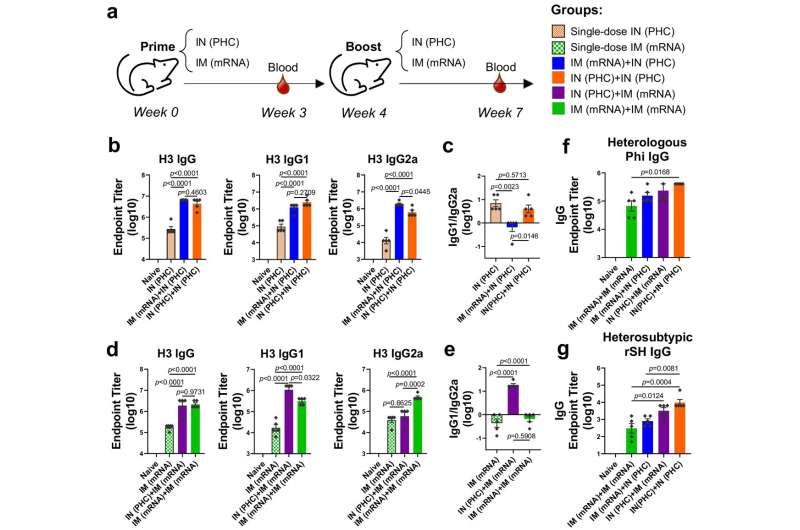
Within the examine, the researchers investigated the consequences of immunization methods on the era of cross-protective immune responses in feminine mice utilizing mRNA lipid nanoparticle (LNP) and protein-based polyethyleneimine-HA/CpG (PHC) nanoparticle vaccines focusing on influenza hemagglutinin. The mice had been immunized with both intramuscular mRNA LNP or intranasal PHC vaccines in a typical prime-plus-boost routine. A wide range of sequential immunization methods had been included on this examine for parallel comparability.
“We demonstrated that cellular and mucosal immune responses are pivotal correlates of cross-protection against influenza,” stated Dr. Baozhong Wang, senior writer of the examine and a Distinguished College Professor within the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State.
“Notably, intranasal PHC immunization outperforms its intramuscular counterpart in inducing mucosal immunity and conferring cross-protection. Sequential mRNA LNP prime and intranasal PHC boost demonstrated optimal cross-protection against antigenically drifted and shifted influenza strains.”
The examine highlights the significance of immunization orders and signifies that in a sequential immunization, an mRNA vaccine priming performs an essential function in steering the Th1/Th2 immune responses. Additionally, the intranasal PHC enhance is essential to the induction of mucosal immunity, Wang stated.
Extra authors of the examine embody Wandi Zhu, Lai Wei, Joo Kyung Kim, Yao Ma and Sang-Moo Kang of the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State.
Extra info:
Chunhong Dong et al, Enhancing cross-protection towards influenza by heterologous sequential immunization with mRNA LNP and protein nanoparticle vaccines, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50087-5
Offered by
Georgia State College
Quotation:
Examine: Nanoparticle vaccines improve cross-protection towards influenza viruses (2024, July 10)
retrieved 10 July 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-07-nanoparticle-vaccines-influenza-viruses.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.

