Wounds which are superficial for some will be life-threatening for others. With diabetic wounds, therapeutic will be gradual, notably within the toes, growing the tissue’s susceptibility to an infection. Foot ulcers and different diabetic foot issues have related mortality charges to some cancers, but progress towards improved remedies has plateaued. Now, researchers could have discovered a greater method to kickstart the therapeutic course of.
Arizona State College (ASU) bioengineers have developed a multistep technique that applies totally different nanomaterials to wounds at totally different occasions to help each early- and late-stage therapeutic. In a examine printed within the journal Biomaterials, the authors’ methodology outperformed a typical wound dressing in a diabetic mouse mannequin, closing wounds sooner and producing extra sturdy pores and skin tissue.
“Healing a wound is like building a house. You have to lay the foundation first before you can put in the plumbing,” mentioned co-first writer Jordan Yaron, Ph.D., a bioengineering assistant analysis professor at ASU. “With our approach, we’re mindful of which stage the wound is in. Providing the right treatment at the right time is key.”
The researchers’ evaluation additionally means that their method unexpectedly activated an immune cell inhabitants not usually seen in wounds that may resolve irritation, which highlights a brand new potential avenue to speed up therapeutic.
A multifaceted resolution for a multifaceted drawback
Clinically, the usual observe for wounds is to maintain them clear and use a dressing to guard them whereas they heal. This method will get the job completed for many accidents however falls brief for sufferers with situations that intervene with the therapeutic course of, reminiscent of diabetes. Along with inflicting poor circulation and neuropathy, diabetes can disrupt wound therapeutic by impairing the operate of varied immune cells.
The researchers devised a method to deal with wounds like these and in contrast it to a generally used dressing in a diabetic mouse mannequin.
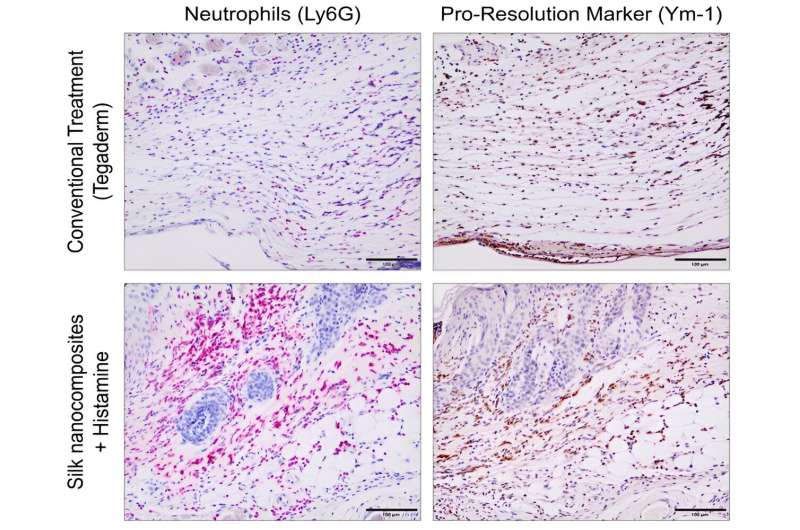
For step one, the group fabricated a silk nanomaterial dressing embedded with gold nanorods. As a result of gold nanoparticles readily convert gentle to warmth, the group was in a position to direct a laser at dressings positioned over recent wounds in mice, producing warmth that rapidly sealed them in place and supplied a excessive stage of safety.
The technique, which the authors beforehand discovered success with, creates one thing akin to an instantaneous scab, Yaron defined. This time round, the authors added histamine to the combo, a pure biochemical produced by the immune system that performs necessary roles in irritation, blood vessel growth, and allergic reactions.
Irritation dominates the physique’s preliminary response to accidents, however ultimately subsides to permit the physique to rebuild. Nonetheless, diabetic wounds can get caught in first gear, sustaining persistent, low-grade irritation, which might inhibit the therapeutic course of.

“Since the wound is stalled, we wanted to co-deliver histamine with the dressing, to give a push and bring the inflammation stage to a resolution. Then we could introduce another strategy to take care of the subsequent phases of healing,” mentioned senior and corresponding writer Kaushal Rege, Ph.D., a chemical engineering professor at ASU.
The authors monitored the wounded mice for 11 days and located that animals handled with a mixture of the nanomaterial dressing and histamine healed on the quickest fee in comparison with these handled with the usual dressing with histamine or the nanomaterial dressing alone.
The researchers mechanically examined the healed pores and skin as effectively, discovering that the tissue handled with each the nanomaterial and histamine was strongest and most much like unwounded pores and skin.
How precisely did the remedy velocity up the method so drastically? For a greater understanding, the group analyzed tissue samples by assessing gene expression and inspecting cells below the microscope.
They discovered {that a} particular immune cell kind, N2 neutrophils, have been extremely prevalent in handled wounds as much as seven days post-injury. As the primary responders of the immune system, these cells normally filter inside a day or two, making their presence within the wound after every week extremely uncommon. However since they’re identified to supply histamine and different reparative molecules, additionally it is doable that these immune cells are the linchpin of the remedy, famous Yaron.
The group plans to dig deeper into the reason for the neutrophils’ presence in addition to their position in wound therapeutic.
The investigators’ subsequent step within the examine was to see if they may enhance therapeutic additional by accelerating the post-inflammation part whereby cells proliferate and rework pores and skin tissue.
In a second set of mice, the authors adopted up their preliminary remedy with a pair of nanoparticles they beforehand developed that have been derived from two explicit progress elements—proteins native to the physique that promote the formation of pores and skin tissue.
The group injected the nanoparticles at numerous time factors into the nanomaterial-dressed wound mattress, discovering that supply on day six had one of the best outcomes almost about wound closure and tissue energy. This time level corresponds to a transitionary part wherein cells start proliferating and reworking tissue.
With promising ends in mice behind them, the authors are actually testing their technique in bigger animal fashions extra related to human well being, reminiscent of pigs.
“The authors put together previously existing components in a unique way. By considering the timing of bioactive delivery and analyzing the immune response, the team put forth an impressive study. I believe they are in a good position moving forward,” mentioned David Rampulla, Ph.D., director of the Division of Discovery Science and Know-how on the Nationwide Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB).
Extra info:
Deepanjan Ghosh et al, Bioactive nanomaterials kickstart early restore processes and potentiate temporally modulated therapeutic of wholesome and diabetic wounds, Biomaterials (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122496
Supplied by
Nationwide Institutes of Well being
Quotation:
A nanomaterial one-two punch rapidly heals wounds in diabetic animal mannequin (2024, Could 31)
retrieved 1 June 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-05-nanomaterial-quickly-wounds-diabetic-animal.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

