Researchers from the Laboratory for Idea and Simulation of Supplies at EPFL in Lausanne, a part of the NCCR MARVEL, have used computational strategies to establish what could possibly be the thinnest doable metallic wire, in addition to a number of different unidimensional supplies with properties that would show fascinating for a lot of functions.
Unidimensional (or 1-D) supplies are one of the crucial intriguing merchandise of nanotechnology and are fabricated from atoms aligned within the type of wires or tubes. Their electrical, magnetic, and optical properties make them wonderful candidates for functions starting from microelectronics to biosensors to catalysis.
Whereas carbon nanotubes are the supplies which have acquired many of the consideration to date, they’ve proved very tough to fabricate and management, so scientists are keen to seek out different compounds that could possibly be used to create nanowires and nanotubes with equally fascinating properties, however simpler to deal with.
So, Chiara Cignarella, Davide Campi and Nicola Marzari thought to make use of laptop simulations to parse recognized three-dimensional crystals, on the lookout for those who—based mostly on their structural and digital properties—seem like they could possibly be simply “exfoliated,” basically peeling away from them a steady 1-D construction. The identical technique has been efficiently used prior to now to check 2D supplies, however that is the primary utility to their 1-D counterparts.
The researchers began from a group of over 780,000 crystals, taken from varied databases discovered within the literature and held collectively by van der Waals forces, the form of weak interactions that occur when atoms are shut sufficient for his or her electrons to overlap. Then they utilized an algorithm that thought-about the spatial group of their atoms on the lookout for those that integrated wire-like buildings, and calculated how a lot vitality could be essential to separate that 1-D construction from the remainder of the crystal.
“We were looking specifically for metallic wires, which are supposed to be difficult to find because 1-D metals, in principle, should not be sufficiently stable to allow for exfoliation,” says Cignarella, who’s the primary writer of the paper.
In the long run, they got here up with a listing of 800 1-D supplies, out of which they chose the 14 finest candidates—compounds that haven’t been synthesized as precise wires but, however that simulations counsel as possible. They then proceeded to compute their properties in higher element, to confirm how steady they’d be and what digital habits one ought to count on of them.
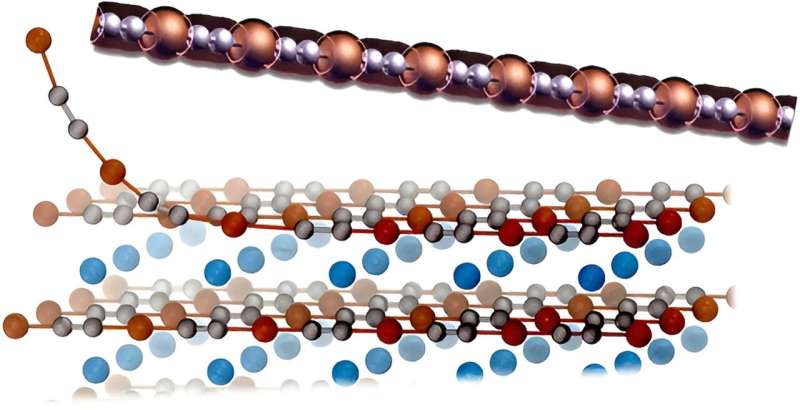
4 supplies—two metals and two semi-metals—stood out as probably the most fascinating ones. Amongst them is the metallic wire CuC2, a straight-line chain composed by two carbon atoms and one copper atom, the thinnest metallic nanowire steady at 0 Okay discovered to date.
“It’s really interesting because you would not expect an actual wire of atoms along a single line to be stable in the metallic phase,” says Cignarella. The scientists discovered that it could possibly be exfoliated from three totally different guardian crystals, all recognized from experiments (NaCuC2, KCuC2 and RbCuC2). It requires little vitality to be extracted from them, and its chain could be bended whereas preserving its metallic properties, which might make it fascinating for versatile electronics.
Different fascinating supplies discovered within the examine, which is printed in ACS Nano, embody the semi-metal Sb2Te2, which due to its properties, could permit for learning an unique state of matter predicted 50 years in the past however by no means noticed, known as excitonic insulators, a kind of uncommon instances the place quantum phenomena develop into seen on the macroscopic scale. Then there are Ag2Se2, one other semi-metal, and TaSe3, a widely known compound that’s the just one to have already been exfoliated in experiments as a nanowire, and that the scientists used as a benchmark.
As for the longer term, Cignarella explains that the group needs to crew with experimentalists to really synthesize the supplies, whereas persevering with computational research to see how they transport electrical costs and the way they behave at totally different temperatures. Each issues will probably be basic to understanding how they’d carry out in real-world functions.
Extra info:
Chiara Cignarella et al, Looking for the Thinnest Metallic Wire, ACS Nano (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.3c12802
Supplied by
Nationwide Centre of Competence in Analysis (NCCR) MARVEL
Quotation:
A sequence of copper and carbon atoms will be the thinnest metallic wire (2024, June 11)
retrieved 11 June 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-06-chain-copper-carbon-atoms-thinnest.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.

