Think about a skinny movie, simply nanometers thick, that might retailer gigabytes of knowledge—sufficient for motion pictures, video video games, and movies. That is the thrilling potential of ferroelectric supplies for reminiscence storage. These supplies have a singular association of ions, leading to two distinct polarization states analogous to 0 and 1 in binary code, which can be utilized for digital reminiscence storage.
These states are steady, which means they’ll ‘bear in mind’ knowledge with out energy, and may be switched effectively by making use of a small electrical subject. This property makes them extraordinarily energy-efficient and able to quick learn and write speeds. Nonetheless, some well-known ferroelectric supplies, corresponding to Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 (PZT) and SrBi2Ta2O9, degrade and lose their polarization when uncovered to warmth therapy with hydrogen throughout fabrication.
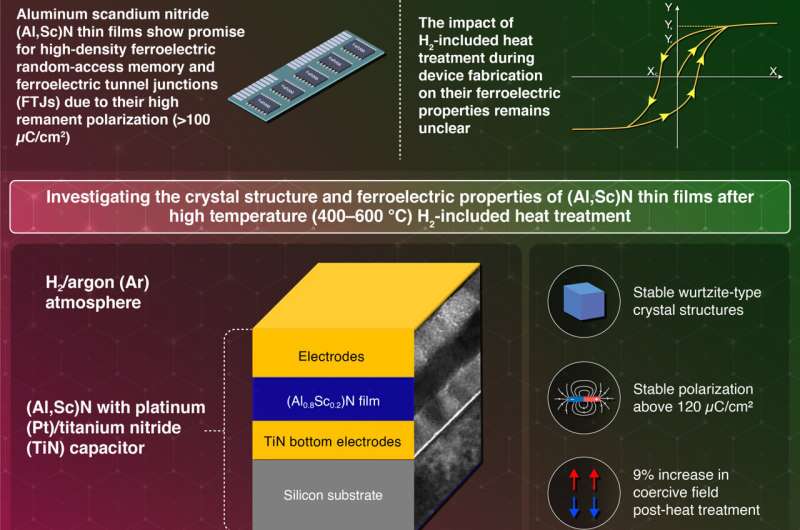
In a research printed within the journal Utilized Physics Letters, a analysis staff led by Assistant Professor Kazuki Okamoto and Hiroshi Funakubo at Tokyo Institute of Expertise (Tokyo Tech), in collaboration with Canon ANELVA Company and Japan Synchrotron Radiation Analysis Institute (JASRI), has proven that aluminum scandium nitride (AlScN) ferroelectric movies stay steady and preserve their ferroelectric properties at temperatures as much as 600°C.
“Our results attest to the high stability of the ferroelectricity of the films subjected to heat treatment in hydrogen-included atmosphere, regardless of the electrode material. This is a highly promising result for next-generation ferroelectric memory devices and offers more processing options,” says Funakubo.
For ferroelectric supplies to be appropriate with high-temperature fabrication processes below an H2-included ambiance, they ideally ought to expertise little to no degradation of their crystal construction and ferroelectric properties. Two essential parameters on this regard are remnant polarization (Pr) and coercive subject (Ec). Pr refers back to the polarization retained after eradicating the electrical subject, whereas Ec is the electrical subject required to change the fabric’s polarization state.
AlScN has the next Pr (>100 µC/cm²) than PZT (30–50 µC/cm²). Nonetheless, the impression of warmth therapy below an H2-included ambiance on its properties was unclear till now.
To analyze this, the researchers deposited (Al0.8Sc0.2)N movie on a silicon substrate utilizing sputtering at 400°C. The movies had been positioned between two electrodes of platinum (Pt) and titanium nitride (TiN). Electrodes play a vital position within the materials’s stability. Pt encourages the incorporation of hydrogen gasoline into the movie, whereas TiN acts as a barrier to H₂ diffusion. So, evaluating its efficiency with completely different electrode supplies is essential.
The movies underwent post-heat-treatment in a hydrogen and argon ambiance for half-hour at temperatures starting from 400 to 600 °C at 800 Torr. The researchers used X-ray diffraction (XRD) to look at adjustments within the crystal construction within the bulk and the film-electrode interface. Constructive-up-negative-down (PUND) measurements had been used to judge Pr and Ec. This system entails making use of constructive and detrimental electrical fields to the movie and observing the ensuing polarization response.
The movies maintained a steady wurtzite-type crystal construction. Pr remained steady above 120 µC/cm², whatever the electrode or therapy ambiance, a worth 5 instances bigger than HfO2-based movies and thrice bigger than that of PZT. Moreover, Ec elevated solely barely by about 9%. This enhance was attributed to adjustments within the movie’s crystal lattice fixed not as a result of presence of hydrogen or the selection of electrode used. Notably, in contrast to different ferroelectric supplies prone to hydrogen diffusion, the excessive bond vitality between Al and N prevents hydrogen from penetrating the movie.
“The results show that (Al0.8Sc0.2)N is much more resistant to degradation by post-heat treatment than conventional ferroelectric and HfO₂-based ferroelectric films,” says Funakubo. With a comparatively steady crystal construction, a excessive Pr worth, and a small change in Ec, (Al,Sc)N movies are a promising candidate for next-generation ferroelectric reminiscence gadgets.
Extra info:
Nana Solar et al, Excessive stability of the ferroelectricity towards hydrogen gasoline in (Al,Sc)N skinny movies, Utilized Physics Letters (2024). DOI: 10.1063/5.0202063
Supplied by
Tokyo Institute of Expertise
Quotation:
Aluminum scandium nitride movies: Enabling next-gen ferroelectric reminiscence gadgets (2024, July 22)
retrieved 22 July 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-07-aluminum-scandium-nitride-enabling-gen.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.

