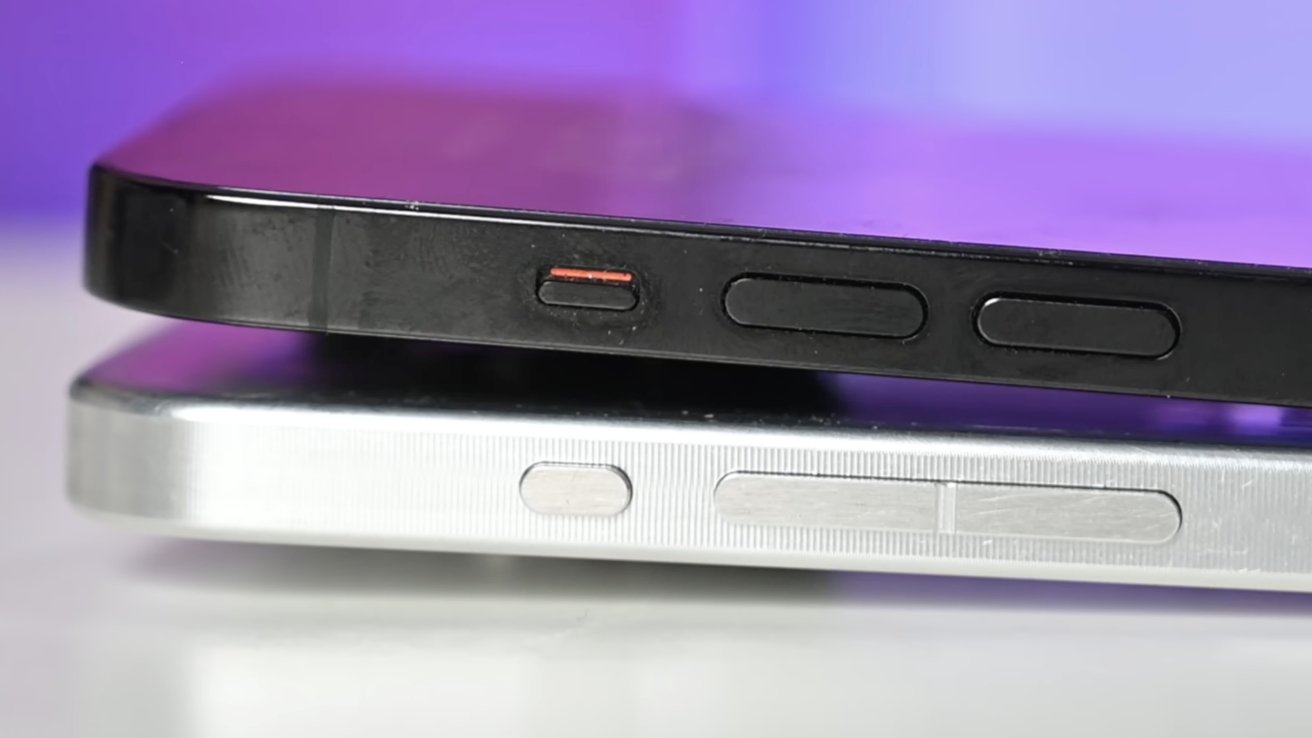
Proto2 items of the iPhone 15 Professional featured a unified haptic quantity button, developed underneath the codename Challenge Bongo

Whether or not a tool is a Mac, iPhone, or iPad, every bit of {hardware} Apple makes must undergo a number of prototype and growth levels. Here is what that appears like, and what Apple calls every stage.
Annually, Apple’s {hardware} prototypes endure a number of rounds of testing to make sure that they’re of ample high quality. This could embody sturdiness testing, drop testing, water resistance testing, reliability, and design viability testing, amongst different issues.
Apple’s prototyping processes are undoubtedly complicated, as checks are carried out on almost each core {hardware} part as a standalone merchandise. Nonetheless, the event of Apple units as a complete follows a extra predictable sample that’s considerably simpler to elucidate.
Preliminary design mock-ups
Earlier than the prototyping and testing of particular person parts can start, Apple first must choose a design for its new {hardware} mission. To perform this, the corporate’s growth groups create many alternative mockups, serving as examples of what the completed product may someday appear like.
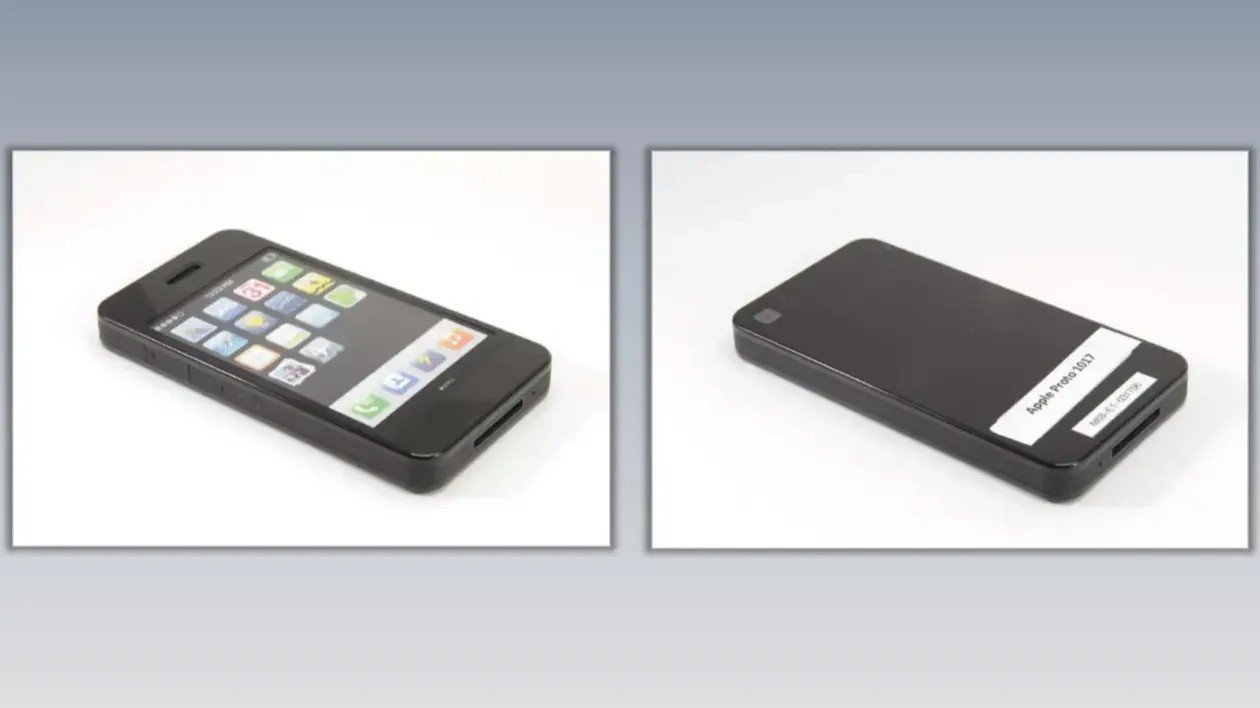

Many early iPhone mockups have been revealed in 2012 throughout Apple’s lawsuit with Samsung
The earliest mockups are usually non-functional, as their sole function is to precisely symbolize a design idea. Due to this, they don’t have any devoted {hardware} parts and usually solely encompass an outdoor casing.
The supplies used for this growth stage can fluctuate relying on the unit in query, the chosen design, and its complexity. Some early mockups of the unique iPhone have been product of polycarbonate, for example, whereas the ultimate mass-production items have been made largely of aluminum and glass.
The authenticity of early Apple mockups is commonly troublesome to establish except the items themselves have an unquestionable connection to the corporate or one in all its staff. If a mockup has an genuine Apple asset tag or a sticker or seems in a ebook, for example, then it’s prone to be authentic.
Lots of Apple’s early iPhone mockups have been unveiled by court docket paperwork in the course of the firm’s lawsuit with Samsung in 2012.
Drop check levels
As soon as Apple settles on an preliminary design for its subsequent product, detailed documentation, product schematics, CAD information, and measurements are despatched to pick manufacturing services and factories. These designs are then checked a number of occasions to make sure that there isn’t a interference between particular person parts.
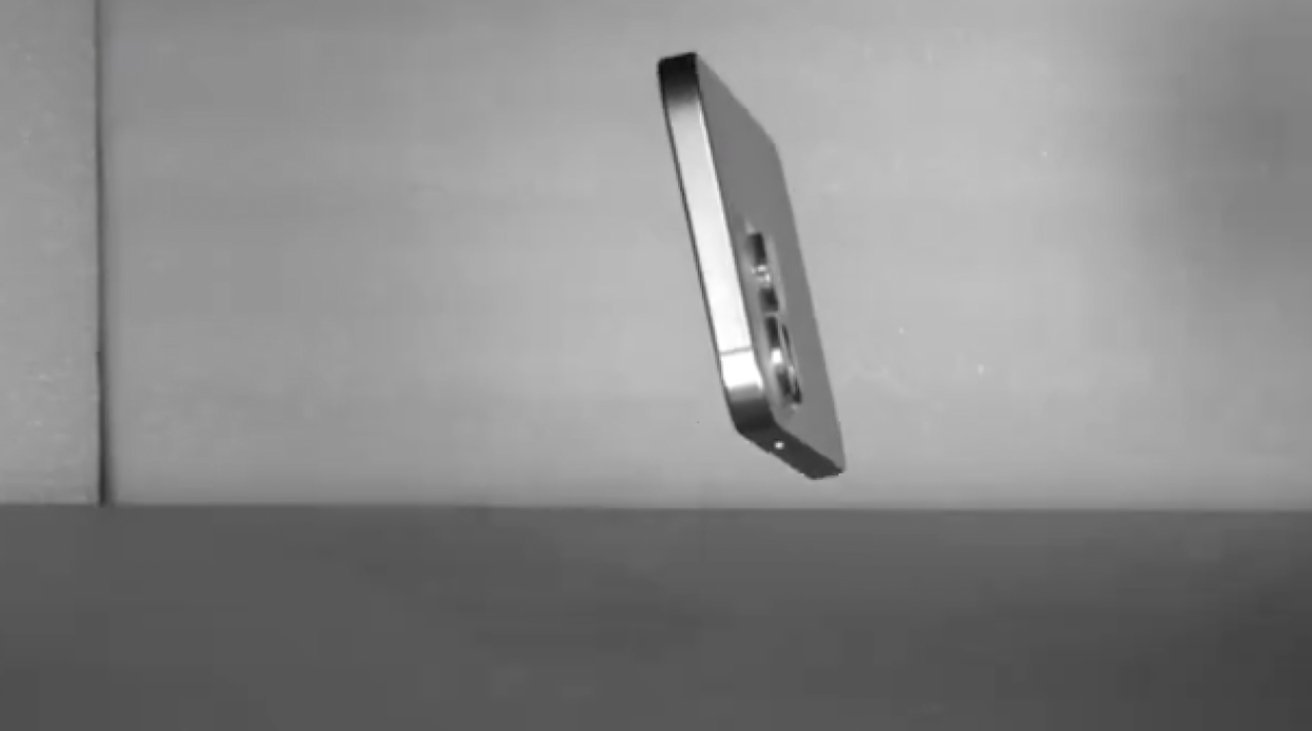

Apple develops devoted prototype levels for drop testing
In some situations, brackets, mounting factors, or different minor particulars could also be altered to make sure that the parts can match collectively as soon as they’re produced and assembled. As soon as a viable check design has been created, preparation for preliminary drop testing begins.
In specialised areas of factories, devoted drop-testing environments with slow-motion cameras and specialised robots are arrange. To calibrate the gear earlier than testing, engineers typically use plastic slabs with the identical dimensions as an upcoming iPhone or iPad.
To make preliminary testing attainable, factories start producing so-called “Drop1” stage units. These encompass core structural parts, such because the machine housing and glass backplate, the place relevant.
These core parts are typically created in a number of colours. That is executed when a key manufacturing course of adjustments, resembling when a brand new coloring method or materials is used for the preliminary batch, and the sturdiness of it must be examined.
Moderately than utilizing absolutely practical {hardware} parts, Drop1 check items characteristic placeholder components. These are sometimes product of machined metallic and may substitute the rear cameras, the battery, and even the glass backplate in some situations.
As soon as the Drop1 items are assembled, they’re then subjected to testing. Units are dropped from particular peak ranges at particular angles, with the outcomes being recorded and analyzed afterward.
Different checks carried out embody dropping the machine right into a plastic tube with metallic obstacles on the within or submerging the machine into liquid to check water resistance. For all checks, parameters, and key knowledge factors are recorded and analyzed after the very fact.
The units themselves are additionally photographed upon the completion of drop testing in order that the ensuing harm can then be analyzed. Main defects, structural issues, or points with the PVD coating course of on the casing are all famous, and suggestions is shipped to the required groups.
As adjustments can happen as a consequence of info gathered from the Drop1 stage, Drop2 units are sometimes produced with alterations or added parts on the within. Related checks are then carried out on Drop2 stage units, and related info is collected.
Proto – the primary try at practical {hardware}
As soon as the preliminary drop check levels are full, the {hardware} mission strikes into the Proto stage of growth. This stage marks the primary try at delivering a completely practical machine with all the required {hardware} parts.
Though Proto-stage items characteristic working {hardware}, they’re merely the primary incarnation of it. Because of this Proto units can have vital variations in comparison with their mass-production counterparts.
These variations can pertain to the surface casing, in some situations, or they’ll influence ports and connectors positioned on the within of the machine. Because of this a Proto-stage machine is perhaps incompatible with mass-production components resembling screens or buttons.
Due to their variations relative to the ultimate product, Proto-stage items are sometimes extremely collectible. They’re additionally troublesome to restore, although, because of mentioned variations and incompatibility with generally out there components and parts.
As this growth stage includes practical {hardware}, much more testing is required to make sure correct performance and long-term sturdiness. Due to this, factories have devoted machines, often called check stations, which check particular person {hardware} parts and sensors inside the units.
Because of this, the Proto stage usually encompasses two sub-stages, often called Proto1 and Proto2, to account for any design adjustments and alterations which will happen as a consequence of info obtained from check outcomes.
Proto1 and Proto2 growth stage items usually run the NonUI variant of iOS. Such a iOS is basically meant for {hardware} testing and is commonly utilized by Apple’s {hardware} engineers and calibration gear.
EVT – Engineering Validation Testing
The subsequent main step after Proto is called EVT, an acronym for Engineering Validation Testing. This growth stage primarily focuses on perfecting the {hardware} and making certain that no hardware-related issues persist.
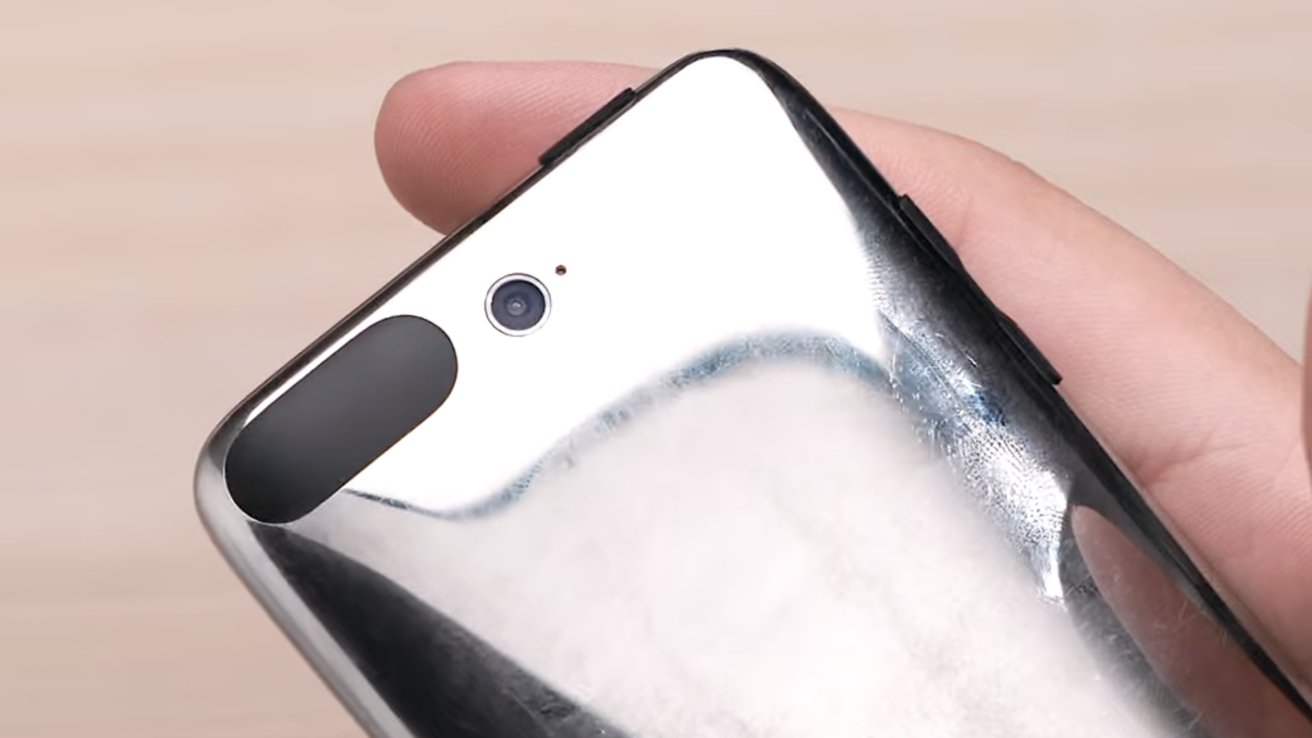

EVT prototypes of the iPod Contact third technology featured a rear digicam, which isn’t current on mass-production items. Picture Credit score: DongleBookPro on YouTube
The EVT stage can embody a number of substages, that are designated numerically, resembling EVT-1, EVT-2, and so forth. These exist to account for particular adjustments made throughout growth, which aren’t giant sufficient to represent a separate growth stage.
For some units, Apple creates letter-based EVT substages. This could occur if a serious drawback is observed later in growth and even on mass-production units. This forces Apple to revert to EVT units for extra testing and growth.
Within the case of the iPod Contact third technology, for example, the mass manufacturing items Apple initially shipped featured a bootrom exploit that would not be simply patched or fastened. Due to this, the corporate created a brand new batch of EVT units with modifications and finally shipped a brand new model of the iPod with an up to date bootrom.
As is the case with Proto1 and Proto2 stage units, EVT prototypes can usually have noticeable design variations in comparison with last mass manufacturing items. EVT items additionally run the identical common working system variant — iOS NonUI.
Within the case of the iPhone 15 Professional, for example, EVT prototypes featured haptic buttons developed underneath the codename Challenge Bongo. Equally, the iPod Contact 3G talked about earlier additionally featured a rear digicam at one level in growth.
Neither of those options might be discovered on the ultimate mass-production items, because the {hardware} was scrapped in each situations for one motive or one other.
DVT – Design Validation Testing
After EVT, the {hardware} mission strikes into the following stage, often called DVT, which is brief for design validation testing. This stage builds upon EVT and ensures that the product has each practical {hardware} in addition to a viable design with no defects or structural issues.

DVT-stage iPhone SE prototype. Picture credit score: AppleDemoYT on YouTube
The DVT stage consists of the identical numerical (DVT-1) and letter-based (DVT-a) substages. There are not any set limits as to what number of substages can fall underneath Design Validation Testing, so it’s attainable to come across prototype units with designations resembling DVT-4.
DVT-stage units usually bear a big resemblance to their mass-production counterparts, with solely minor exterior variations being current, if any. Due to this, Apple sends out DVT-stage units to regulatory authorities, such because the FCC, to substantiate compliance with present requirements and rules pertaining to digital units.
Equally, Apple additionally sends out DVT-stage units to cellphone carriers and community suppliers worldwide to make sure compatibility with main mobile networks. Such units are labeled as CRB, brief for “Carrier Build,” although they’re functionally similar to DVT items in each method.
CRB units usually run a novel variant of iOS often called CarrierOS. Generally, it is a stripped-down model of the InternalUI variant. This implies it contains the usual iOS person interface however with network-related check functions resembling E911Tester.
Generally, DVT-stage units can run both InternalUI or NonUI variations of iOS, relying on the kind of checks they’re used for. The {hardware} of DVT prototypes differs from manufacturing items on the board degree.
Not like mass manufacturing units, DVT and earlier unit units are “development-fused.” This in the end implies that they’ll run further code, and they’re simpler to debug in comparison with manufacturing items, which is why they’re utilized in a number of growth processes.
PVT – Manufacturing Validation Testing
By the PVT stage, the whole design of the brand new {hardware} mission has been finalized. PVT-stage prototypes are just about similar to mass manufacturing items, aside from the truth that they run the NonUI variant of iOS.
The filesystems discovered on PVTE units can typically comprise references to in-development software program options
The PVT stage of growth primarily focuses on perfecting manufacturing procedures. With each product, Apple wants to make sure that the machine might be mass-produced with none points with the items themselves or manufacturing unit gear.
One other variant of PVT machine is the so-called PRQ unit, brief for “Post Ramp Qualification.” These units are examined when Apple introduces a minor change, resembling a brand new colour possibility after launch, and they’re similar to PVT and mass manufacturing items.
As a result of PVT stage items are successfully similar to the ultimate product, these units are price considerably much less to collectors. Their solely redeeming high quality is the truth that they run iOS NonUI.
The one exception to this rule can be PVTE stage units, with the acronym standing for Manufacturing Validation Testing – Engineering.
Not like customary PVT items, that are examined to make sure that mass manufacturing can proceed with out points, PVTE units are utilized by Apple’s software program engineers. Because of this they run the InternalUI variant of iOS, which options the usual iOS person interface, together with in-development options and inner settings.
Because of this, PVTE items can comprise early implementations of software program options years away. A PVTE-stage iPhone Xs Max, for example, contained an early model of Apple’s on-device e-mail categorization characteristic which solely debuted 5 years later.
MP – Mass Manufacturing units
As soon as all prototyping is accomplished, factories will start mass-producing the brand new machine forward of launch. To make sure that the items shipped are absolutely practical, the {hardware} of every machine is examined earlier than it’s despatched out.

Each mass-produced iPhone unit bought by Apple is an MP-type machine
To facilitate the ultimate check course of, Apple first installs a NonUI model of iOS onto mass manufacturing items in order that staff and check gear can work together with the units. As soon as high quality management testing is full, launch (inventory) iOS is put in, and the items are shipped out to be bought.
Each machine bought legally by Apple to prospects or different third events might be thought of a mass-production machine. Units produced with this function in thoughts are additionally thought of mass-production items and are often called MP-intent.
A few of these units inevitably fail the standard management checks as a consequence of {hardware} malfunctions or main defects that can’t be repaired. They’re thought of high quality management rejects, and the faulty parts are typically despatched out for recycling.
MP units that fail high quality management testing can nonetheless have the NonUI variant of iOS put in, making the logic board considerably extra beneficial to a collector than an ordinary one with the discharge of iOS.
An MP-stage machine working iOS NonUI just isn’t price almost as a lot as DVT or an earlier machine, nonetheless, as a result of it options mass-production {hardware} that may be discovered with relative ease.
What does all of this in the end imply?
Prototypes supply distinctive perception as to how units can change throughout growth. In some situations, Apple abruptly eliminated key {hardware} parts from upcoming units, changing them with extra typical components.
Apple’s many alternative prototype levels additionally function a sign of the corporate’s high quality management practices and excessive manufacturing requirements. New merchandise are examined extensively, by and thru, to make sure that no hardware-related issues attain finish customers.

