Though prevailing knowledge holds that point is operating out, BloombergNEF’s New Power Outlook 2024 seemingly exhibits how the world might nonetheless obtain the key aim of the Paris Settlement – holding international warming to properly under 2°C and avoiding the worst impacts of local weather change – and what it might take to get there. The brand new report signifies that the pace with which clear applied sciences and decarbonization of the ability sector are scaled up is essential.
The New Power Outlook 2024, the report revealed on 21 Might by analysis supplier BloombergNEF, presents two up to date local weather situations, the Internet Zero State of affairs (NZS) and a base case Financial Transition State of affairs (ETS), designed to tell public policymaking, nation local weather ambition and low-carbon transition methods of firms and monetary establishments.
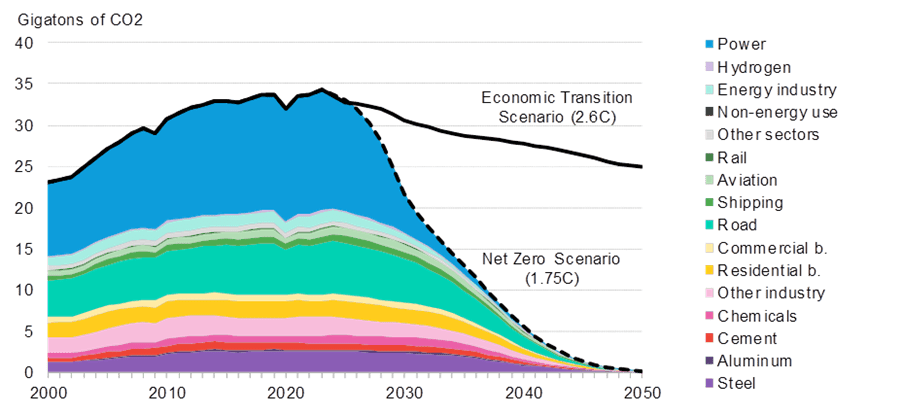
The report’s NZS, which is per a 67% probability of holding international warming to 1.75°C, sees demand for oil, fuel and coal attain an instantaneous peak and fall right into a steep decline ranging from the yr 2025. The ability, transport, business and buildings sectors transition at totally different speeds primarily based on the applied sciences out there for them to decarbonize, however all see emissions begin to fall instantly. These short-term modifications solely come to move because of a speedy scale-up of fresh power applied sciences, particularly a tripling of worldwide renewable-energy capability by 2030, speedy uptake of electrical autos (EVs) resulting in a full international phase-out of combustion engine car gross sales by 2034, and a significant scale-up of carbon seize know-how, alongside power storage and nuclear energy, earlier than 2030.
“The path to staying well below two degrees is narrowing,” stated David Hostert, head of economics and modeling at BNEF and the lead writer of the report. “In the 18 months since we last updated our global scenarios, the energy transition has certainly accelerated – but not nearly enough. This report should serve as a wake-up call: we need a rapid decline in emissions starting from now – not in five years’ time – if net zero by mid-century is to remain a possibility.”
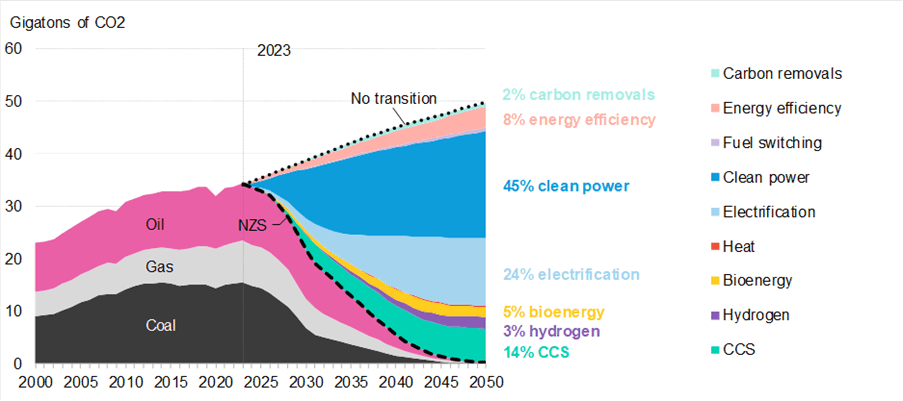
Cleansing up the ability sector accounts for nearly half of emissions averted between at present and 2050, in contrast with a no-transition state of affairs the place there isn’t a additional motion on decarbonization. Electrification of end-use sectors, together with street transport, buildings and business, accounts for the subsequent quarter of emissions. The options wanted to abate the remaining quarter of emissions are among the many most difficult to scale: biofuels in delivery and aviation; hydrogen in business and transport; and carbon seize and storage in business and energy.
The New Power Outlook additionally particulars a base case ETS, by which clean-energy applied sciences are solely deployed the place they’re economically cost-competitive or adopted by client selection, with no additional coverage help for clear applied sciences. The affordability of renewable power, particularly photo voltaic and wind, implies that they develop quickly on this state of affairs, to 51% of worldwide energy technology by 2030, and 70% by 2050. The worldwide energy system is remodeled and turns into rather more versatile as a way to accommodate excessive penetrations of wind and photo voltaic.
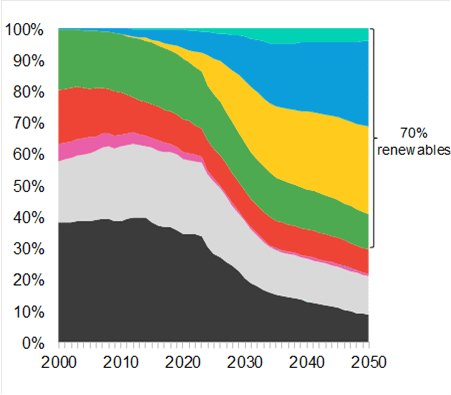
“Our hourly modeling shows that power systems can accommodate very high penetrations of wind and solar without incurring higher costs,” stated Ian Berryman, lead power techniques modeler at BNEF. “With the aid of smart electric vehicle charging, battery storage and flexible generators, the most affordable power system of the future will be one based on a foundation of inexpensive renewables.”
The ETS additionally sees vital EV uptake, because of their rising cost-competitiveness in comparison with typical autos. Because of the mixed impacts of fresh energy, EVs and power effectivity, emissions in 2050 within the ETS are half what they’d in any other case be with out these applied sciences, or down 27% from present ranges. That is removed from attaining internet zero – and breaches the Paris Settlement with a worldwide warming results of 2.6°C – however demonstrates how far the power transition can already go primarily based on economical and commercially prepared applied sciences. On this state of affairs, fossil fuels nonetheless play an necessary position in energy, business, transport and buildings sectors, however fuel demand grows modestly whereas oil and coal demand are set to enter a interval of structural decline.
Matthias Kimmel, head of power economics at BNEF, stated, “Renewable energy, electric vehicles and energy storage are already being deployed at scale and will only grow further in the next few years. These three technologies are no-regrets choices that can help countries reduce emissions, improve energy security and even reduce energy system costs today.”
BNEF has enhanced its modeling for the 2024 version of the New Power Outlook. The evaluation now contains detailed modeling outcomes for 12 international locations and 9 areas for each situations, and exhibits that:
- The present local weather plans (Nationally Decided Contributions or NDCs) of Brazil, France, the UK, the US and Australia are essentially the most aligned to BNEF’s Internet Zero State of affairs.
- Germany, South Korea, Japan and India have present NDCs which are in step with or higher than the Financial Transition State of affairs – indicating they’ve scope to lift their ambition to align with the NZS.
- China, Indonesia and Vietnam have essentially the most scope to lift ambition of their subsequent Nationally Decided Contributions. Their present NDCs even fall in need of the Financial Transition State of affairs.
The report additionally sheds mild on different necessary subjects regarding the worldwide low-carbon transition, together with:
- The necessity to scale up 9 key applied sciences as a way to get on monitor for internet zero. These are: renewable energy, electrical autos, battery power storage, nuclear power, carbon seize and storage, hydrogen, sustainable aviation fuels, warmth pumps and energy networks.
- A extra nuanced image of the place low-carbon hydrogen could be most impactful within the power transition, and the place electrification plainly makes extra sense.
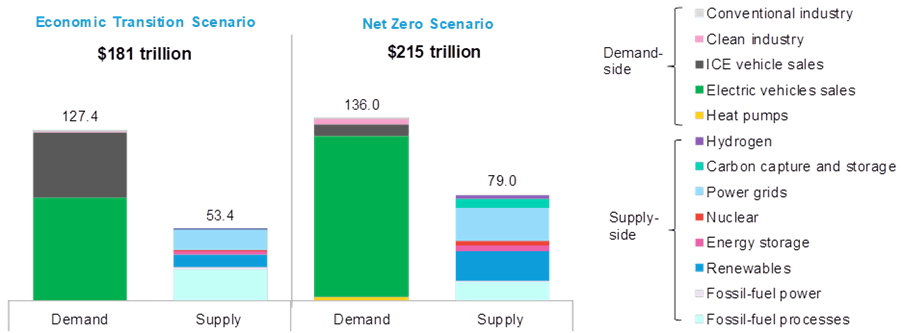
How the applied sciences above mix and work together to resolve for decarbonization throughout energy, transport, business, and buildings. - The funding volumes wanted to realize the ETS ($181 trillion globally to 2050) and the NZS ($215 trillion to 2050), and why these estimates are surprisingly comparable (solely 19% larger within the NZS).
- The significance of land-use issues, provided that low-carbon applied sciences sometimes require a bigger land footprint than fossil-based sources, and the rising land calls for for power transition, meals manufacturing and biodiversity preservation will have to be weighed up and co-optimized.