Earth’s ambiance holds an ocean of water, sufficient liquid to fill Utah’s Nice Salt Lake 800 instances. Extracting a few of that moisture is seen as a possible manner to supply clear consuming water to billions of individuals globally who face persistent shortages.
Current applied sciences for atmospheric water harvesting (AWH) are saddled with quite a few downsides related to dimension, value and effectivity. However new analysis from College of Utah engineering researchers has yielded insights that would enhance efficiencies and produce the world one step nearer to tapping the air as a culinary water supply in arid locations.
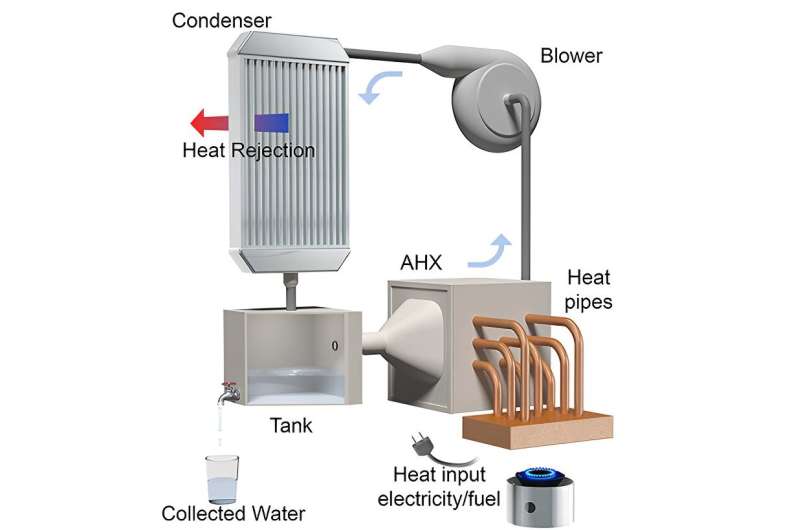
The research unveils the first-of-its-kind compact fast biking fuel-fired AWH gadget. This two-step prototype depends on adsorbent supplies that draw water molecules out of non-humid air, then applies warmth to launch these molecules into liquid kind, in keeping with Sameer Rao, senior creator of the printed within the journal Cell Reviews Bodily Science and an assistant professor of mechanical engineering.
“Hygroscopic materials intrinsically have affinity to water. They soak up water wherever you go. One of the best examples is the stuff inside diapers,” stated Rao, who occurs to be the daddy of an toddler son. “We work with a specific type of hygroscopic material called a metal organic framework.”
Rao likened steel natural frameworks to Lego blocks, which could be rearranged to construct all types of buildings. On this case, they’re organized to create a molecule best for gasoline separation.
“They can make it specific to adsorb water vapor from the air and nothing else. They’re really selective,” Rao stated. Developed with graduate pupil Nathan Ortiz, the research’s lead creator, this prototype makes use of aluminum fumarate that was customary into panels that acquire the water as air is drawn by.
“The water molecules themselves get trapped on the surfaces of our material, and that’s a reversible process. And so instead of becoming ingrained into the material itself, it sits on the walls,” Ortiz stated. “What’s special about these absorbent materials is they have just an immense amount of internal surface area. There’s so many sites for water molecules to get stuck.”
Only a gram of this materials holds as a lot floor space as two soccer fields, in keeping with Rao. So just a bit materials can seize quite a lot of water.
“All of this surface area is at the molecular scale,” Rao stated. “And that’s awesome for us because we want to trap water vapor onto that surface area within the pores of this material.”
Assist for the analysis got here from the DEVCOM Soldier Middle, a program run by the Division of Protection to facilitate expertise switch that helps Military modernization. The Military’s curiosity within the mission stems from the necessity to preserve troopers hydrated whereas working in distant areas with few water sources.
“We specifically looked at this for defense applications so that soldiers have a small compact water generation unit and don’t need to lug around a large canteen filled with water,” Rao stated. “This would literally produce water on demand.”
Rao and Ortiz have filed for a preliminary patent primarily based on the expertise, which addresses non-military wants as properly.

“As we were designing the system, I think we also had perspective of the broader water problem. It’s not just a defense issue, it’s very much a civilian issue,” Rao stated. “We think in terms of water consumption of a household for drinking water per day. That’s about 15 to 20 liters per day.”
On this proof of idea, the prototype achieved its goal of manufacturing 5 liters of water per day per kilogram of adsorbent materials. In a matter of three days within the discipline, this gadget would outperform packing water, in keeping with Ortiz.
Within the gadget’s second step, the water is precipitated into liquid by making use of warmth utilizing a standard-issue Military tenting range. This works due to the exothermic nature of its water accumulating course of.
“As it collects water, it’s releasing little bits of heat. And then to reverse that, we add heat,” Ortiz stated. “We just put a flame right under here, anything to get this temperature up. And then as we increase the temperature, we rapidly release the water molecules. Once we have a really humid airstream, that makes condensation at ambient temperature much easier.”
Nascent applied sciences abound for atmospheric water harvesting, which is extra simply completed when the air is humid, however none has resulted in tools that may be put to sensible use in arid environments. Ortiz believes his gadget could be the primary, primarily as a result of it’s powered with energy-dense gasoline just like the white gasoline utilized in tenting stoves.
The staff determined towards utilizing photovoltaics.
“If you’re reliant on solar panels, you’re limited to daytime operation or you need batteries, which is just more weight. You keep stacking challenges. It just takes up so much space,” Ortiz stated. “This technology is superior in arid conditions, while refrigeration is best in high humidity.”
Extra info:
Nathan P. Ortiz et al, Compact fast biking fuel-fired atmospheric water harvesting gadget for all-day water manufacturing, Cell Reviews Bodily Science (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2024.102115
College of Utah
Quotation:
Compact atmospheric water harvesting gadget can produce water out of skinny air (2024, July 23)
retrieved 23 July 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-07-compact-atmospheric-harvesting-device-thin.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

