Blue power has the potential to supply a sustainable different to fossil fuels. In easy phrases, it includes harnessing the power produced when the ions in a salt resolution transfer from excessive to low concentrations.
A staff together with researchers from Osaka College has probed the impact of voltage on the passage of ions via a nanopore membrane to reveal larger management of the method.
In a research not too long ago revealed in ACS Nano the researchers checked out tailoring the circulate of ions via the array of nanopores that make up their membrane, and the way this management might make making use of the expertise on a big scale a actuality.
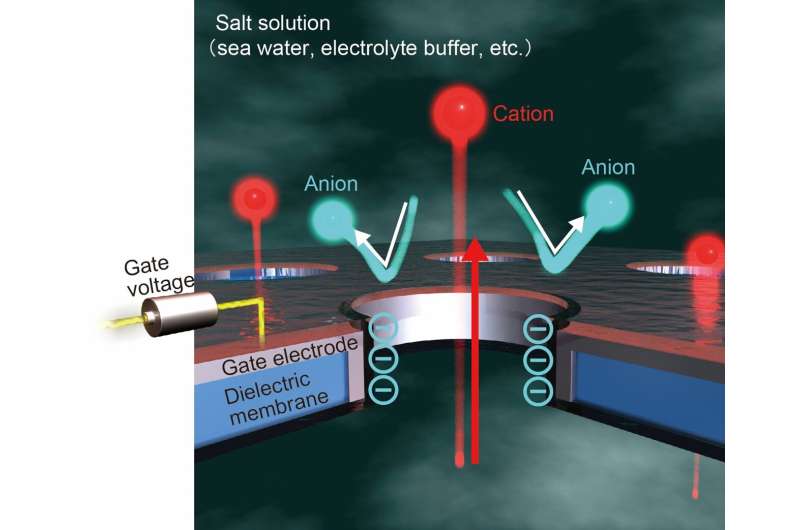
If the membranes are constituted of a charged materials, nanopores could cause a present to circulate via them by attracting resolution ions with the other cost. The ions with the identical cost can then transfer via the pore producing the present. Which means the pore materials is essential and selecting it has been the technique of controlling the circulate and present so far.
Nonetheless, producing the very same pore constructions in a variety of various supplies to grasp their comparative performances is difficult. The researchers subsequently determined to research one other method of tailoring the circulate of ions throughout nanopore membranes.
“Instead of simply using the basic surface charge of our membrane to dictate the flow, we looked at what happens when voltages are applied,” explains research lead creator Makusu Tsutsui. “We used a gate electrode embedded across the membrane to control the field through voltage in a similar way to how semiconductor transistors work in conventional circuits.”
The researchers discovered that with no voltage utilized there was no cost generated by the circulate of cations—positively charged ions—as a result of they had been interested in the negatively charged membrane floor.
Nonetheless, if completely different voltages had been utilized, this efficiency may very well be tuned to permit cations to circulate, even offering full selectivity for cations. This led to a six-fold enhance within the osmotic power effectivity.
“By enhancing the charge density at the surface of the nanopores that make up the membrane, we achieved a power density of 15 W/m2,” says senior creator Tomoji Kawai. “This is very encouraging in terms of progressing the technology.”
The research findings reveal the potential for scaling nanopore membranes for on a regular basis utility. It’s hoped that nanopore osmotic energy turbines will present a way of bringing blue power to the mainstream for a extra sustainable power future.
Extra data:
Makusu Tsutsui et al, Gate-All-Round Nanopore Osmotic Energy Turbines, ACS Nano (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.4c01989
Supplied by
Osaka College
Quotation:
Controlling ion transport for a blue power future: Analysis highlights the potential of nanopore membranes (2024, Could 30)
retrieved 30 Could 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-05-ion-blue-energy-future-highlights.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

