Unplanned downtime is costing the world’s largest firms $400 billion a 12 months, or roughly 9% of their earnings, a brand new report has discovered. That is the equal of about $9,000 misplaced for each minute of system failure or service degradation.
The report, revealed by the information administration platform Splunk, additionally revealed that it takes 75 days for income for a Forbes World 2000 firm to get well to the place it stood financially previous to the incident.
Downtime immediately ends in monetary losses by misplaced income, regulatory fines and extra time wages for workers rectifying the difficulty. The report additionally unveiled hidden prices that take longer to have an effect, like diminished shareholder worth, stagnant developer productiveness and reputational injury.
The Hidden Prices of Downtime report surveyed 2,000 executives, together with CFOs, CMOs, engineers, and IT and safety professionals, from World 2000 firms in 53 international locations and a spread of industries. They offered perception into the place downtime originated, the way it affected their companies and the best way to scale back it.
Causes of downtime contains cybersecurity-related human errors
Downtime incidents skilled by giant firms might be positioned in certainly one of two classes: safety incidents (e.g., phishing assaults) or utility or infrastructure points (e.g., software program failures). The common World 2000 agency sees 466 hours of cybersecurity-related downtime and 456 hours of utility or infrastructure-related downtime, based on the report.
“While availability for most systems is at multiple 9s, downtime across hundreds — or perhaps thousands — of systems adds up,” the authors wrote.
The primary largest reason for downtime incidents cited by the respondents was cybersecurity-related human errors, akin to clicking a phishing hyperlink. This was adopted by ITOps-related human errors (e.g., infrastructure misconfigurations, capability points and utility code errors). It takes a mean of 18 hours till downtime or service degradation on account of human error, like latency, is detected and an extra 67 to 76 hours to get well.
SEE: How one can Stop Phishing Assaults with Multi-Issue Authentication
Software program failure is the third main reason for downtime, which turns into extra of a danger as organisations undertake extra complicated improvement and deployment practices. Fourth is malware assault.
The report revealed that greater than half of executives are conscious of root causes of downtime of their organisations however select to not repair them. This can be as a result of they don’t need to enhance the technical debt of legacy methods or have a plan to decommission the problematic utility. Moreover, solely 42% of know-how executives decide to have a postmortem after a downtime incident to isolate and alleviate the trigger, as they are often troublesome and time-consuming.

Direct prices of downtime
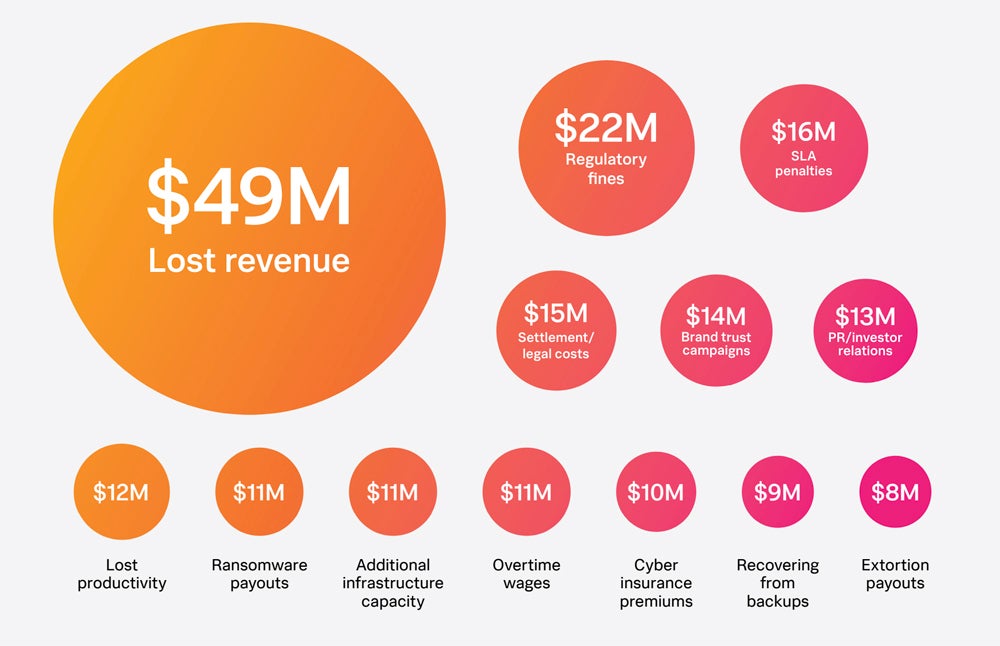
Misplaced income is by far the most important value on account of a downtime occasion, at a mean of $49 million a 12 months for every World 2000 firm. The second largest is regulatory fines at $22 million, as many localities place strict laws on downtime, such because the Digital Operational Resilience Act for the E.U.’s monetary sector.
Different vital value sinks embrace repairing the model’s popularity. In line with the CMOs, it prices a mean of $14 million to conduct the mandatory model belief campaigns and one other $13 million to restore public, investor and authorities relations. It takes about 60 days to totally restore the model’s well being.
Regardless of recommendation from cyber professionals, 67% of CFOs advocate their board of administrators pay the ransom to get out of a ransomware assault, both on to the perpetrator, by insurance coverage, a 3rd social gathering or all three. Payouts value World 2000 firms a complete of $19 million yearly.
Hidden prices of downtime
Past the speedy monetary prices of downtime, respondents cited a lot of different pricey ripple results. For instance, 28% mentioned {that a} downtime occasion decreased their shareholder worth, with a mean of a 2.5% inventory worth drop. It took a mean of 79 days for a big firm’s inventory to get well to the place it was beforehand.
Different hidden prices of downtime occasions embrace delayed time-to-market and stagnated developer innovation, cited by 74% and 64% of respondents, respectively. The latter is a results of technical groups shifting from high-value work to making use of patches and taking part in postmortems. Equally, in advertising and marketing departments, downtime ends in groups and budgets being pivoted to disaster administration, so productiveness is misplaced in different areas.
Buyer-lifetime worth can be affected by downtime, based on 40% of respondents, as an outage will negatively influence the client expertise and, due to this fact, their loyalty to the organisation. In truth, 29% of surveyed firms say they know they’ve misplaced clients on account of an incident.
SEE: What the AT&T Outage Can Train Organizations About Buyer Communication and IT Finest Practices
How companies can keep away from downtime
Ideas from resilience leaders
The Splunk report revealed a lot of ways in which firms can keep away from downtime, both as a result of respondents deemed them useful or they had been demonstrated by the highest 10% of firms demonstrating resilience to outages.
Corporations within the latter class, so-called “resilience leaders,” retain $17 million extra of their income, pay $10 million much less in fines and save $7 million on ransomware payouts. In addition they get well 23% and 28% sooner than common from cybersecurity and utility or infrastructure-related downtime, respectively. Hidden prices, like poor buyer expertise, have much less of an influence consequently.
Resilience leaders make investments extra in sure areas than different organisations surveyed, and these are:
- Safety instruments: $12 million extra.
- Observability instruments: $2.4 million extra.
- Extra infrastructure capability: $8 million extra.
- Cyber insurance coverage premiums: $11 million extra.
- Backups: $10 million extra.
Generative AI can be used to cut back downtime, as it may possibly equip groups with the knowledge they should get again on-line rapidly. The report discovered that resilience leaders broaden their use of AI options 4 instances sooner than different respondents. Moreover, 74% of companies that use discrete AI instruments and 64% who embed AI into current instruments, to deal with downtime deemed it useful.
Ideas from Splunk
The studies’ authors additionally offered tricks to keep away from downtime based mostly on their experience.
- Have a downtime plan. Instrument each app, comply with a runbook for outages and determine proudly owning engineers. Observe tabletop workouts and drills.
- Carry out postmortems. Observability tooling makes it simpler to isolate root causes and implement fixes.
- Set up a transparent knowledge governance coverage. Guidelines relating to mental property, particularly in terms of inputting it into giant language fashions, will safeguard the organisation from knowledge leakage.
- Join groups and instruments. Groups that share instruments, knowledge and context could have a better time collaborating, fixing the issue and figuring out the basis reason for downtime.
- Make use of predictive analytics. AI- and ML-driven options can recognise patterns and alert groups when downtime could happen.
“Disruption in business is unavoidable. When digital systems fail unexpectedly, companies not only lose substantial revenue and risk facing regulatory fines, they also lose customer trust and reputation,” mentioned Gary Steele, President of Go-to-Marketplace for Cisco and GM at Splunk, in a press launch.
“How an organisation reacts, adapts and evolves to disruption is what sets it apart as a leader. A foundational building block for a resilient enterprise is a unified approach to security and observability to quickly detect and fix problems across their entire digital footprint.”

