A brand new research performed by the Wilhelm Lab on the College of Oklahoma examines a promising growth in biomedical nanoengineering. Revealed in Superior Supplies, the research explores new findings on the transportation of most cancers nanomedicines into stable tumors.
A frequent false impression about many malignant stable tumors is that they’re comprised solely of cancerous cells. Nevertheless, stable tumors additionally embody wholesome cells, corresponding to immune cells and blood vessels. These blood vessels are nutrient transportation highways that tumors have to develop, however they will also be a pathway for medication supply, together with for most cancers nanomedicines.
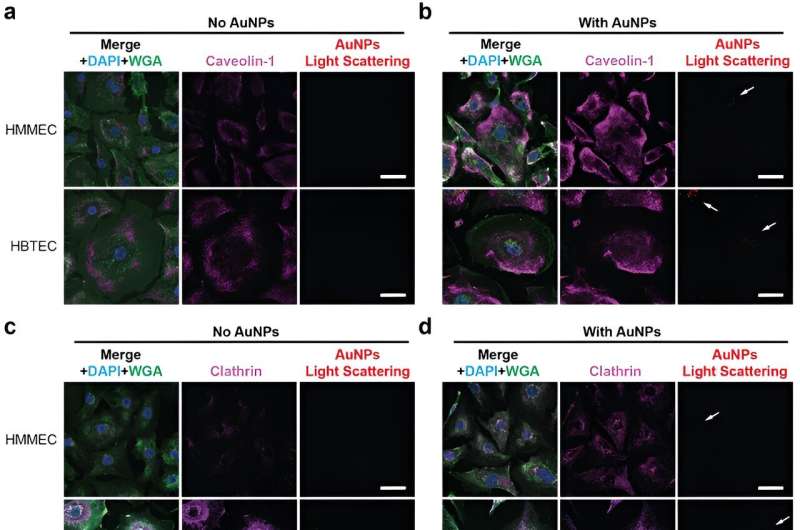
Blood vessels, and the endothelial cells inside them, are the transportation technique examined within the new research led by Lin Wang, Ph.D., who was a postdoctoral analysis affiliate within the Wilhelm Lab whereas conducting the research and is the primary creator of the publication. Endothelial cells line blood vessels and handle the trade between the bloodstream and surrounding tissues. These cells are the primary barrier that the nanotechnologies encounter within the means of being transported into tumors.
The researchers discovered that endothelial cells in breast most cancers tumors are two occasions extra more likely to work together with medicine-carrying nanoparticles than endothelial cells in wholesome breast tissue. Wang mentioned that the tumor endothelial cells have extra transport options than the wholesome endothelial cells, making them ultimate conduits.
“If you know that the same cell type in tumor tissues is two times more likely to interact with your drug carriers than in healthy tissue, then in theory, you should be able to target those cells to get even more nanoparticles delivered into the tumor,” mentioned Stefan Wilhelm, Ph.D., affiliate professor within the Stephenson College of Biomedical Engineering and corresponding creator of the research.
The analysis was performed on endothelial cells remoted from breast most cancers tissues and remoted from wholesome breast tissues. The following steps for the analysis will contain analyzing how the nanoparticles react within the context of the entire tissue structure.
“Cell-culture level experiments are only so good at trying to recapitulate what is happening in the body,” mentioned Wilhelm. “Working with colleagues at OU Health Sciences, we hope to get our hands on not just cells but the entire tumor tissue.”
The analysis group is working with the Stephenson Most cancers Middle to arrange an ethics protocol permitting the lab to entry saved samples of most cancers tissue fairly than simply remoted cells. The Wilhelm Lab is concentrated on learning nanomedicine and utilizing nanoparticles for drug supply and diagnostics. Particularly, the group is concerned with learning the supply of medicine into stable tumor tissues.
From an engineering perspective, a novel benefit of utilizing nanoparticles for drug supply is that they’re small and versatile sufficient to be designed as direct supply autos. In a laboratory setting, the nanoparticles are sometimes designed as tiny spheres and loaded with the required medicine. Then, in clinics, they’re usually administered intravenously to sufferers. These medicine flow into by the bloodstream, and a few of them enter the tumor.
There are challenges related to one of these medication transportation. One is that these nanoparticles flow into all through the physique, and consequently, they accumulate in different organs—known as off-target organs—such because the liver, spleen and kidneys. Since these organs filter blood, they take away the nanoparticles, which are sometimes thought of international objects by the physique.
The sector of nanomedicine has been round for greater than 40 years, and there are tens of hundreds of publications on utilizing nanoparticles to deal with cancers on the preclinical stage. However there’s a disconnect between the variety of preclinical publications and the variety of FDA-approved formulations of nanoparticles which might be truly utilized in clinics.
Of these accepted formulations, a fraction are used for stable tumors, and most deal with liquid tumors, corresponding to leukemia. Wilhelm speculates that that is partially as a result of there’s a lack of full understanding of how the nanoparticle supply course of works.
“And if you don’t understand something fully, it’s hard to develop solutions to those problems,” mentioned Wilhelm.
“Researchers have started to go back to the fundamentals of nanomedicine development to understand the translation from the pre-clinical to the clinical space. Our lab wants to focus on these fundamentals to better understand the field and the delivery mechanisms specifically. If we understand these fundamentals, we can contribute even more to the field,” mentioned Wang.
In response to Wilhelm, the following large query is that this: now that the lab has quantified and proven that endothelial cells usually tend to work together with and transport these nanomedicines, how can that transportation be made extra environment friendly and particular to advance scientific most cancers remedies? As these questions are answered, the alternatives for future advances in most cancers well being care will develop.
“We are just scratching the surface by using breast cancer as our model cancer system, but our findings may be relevant for other types of solid tumors as well,” mentioned Wilhelm.
Extra data:
Lin Wang et al, Major Human Breast Most cancers‐Related Endothelial Cells Favor Interactions with Nanomedicines, Superior Supplies (2024). DOI: 10.1002/adma.202403986
Supplied by
College of Oklahoma
Quotation:
Examine reveals promising growth in cancer-fighting nanotechnologies (2024, Might 20)
retrieved 26 Might 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-05-reveals-cancer-nanotechnologies.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

