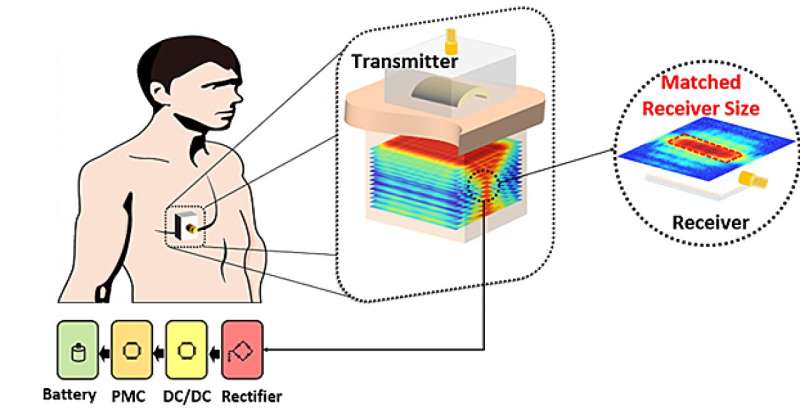
Ultrasound-based wi-fi energy switch is changing into a extra engaging choice to energy implanted biomedical gadgets as a result of it may overcome lots of the limitations and challenges dealing with different wi-fi charging approaches. Now, a brand new research has proven that the form of the implanted receiver can considerably enhance the effectivity of energy harvesting from the ultrasound beam.
Present wi-fi charging applied sciences use both electromagnetic or radio waves to cost the batteries of implanted biomedical gadgets, resembling pacemakers and cochlear implants. However these approaches lose a big quantity of energy touring by way of tissue, making them much less environment friendly for deeper gadgets. They’re additionally related to potential issues, resembling tissue heating and immune results.
Ultrasound can penetrate deeper into tissues with out shedding as a lot vitality or inflicting main unwanted effects. Within the new research, Professor Jin Ho Chang from the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Know-how within the Republic of Korea led a workforce of researchers investigating tips on how to enhance ultrasound vitality harvesting by altering the scale, form and place of the implanted piezoelectric receiver.
They discovered that positioning the receiver inside the focal space of a targeted ultrasound beam considerably elevated the effectivity of the vitality switch. The work is revealed within the journal Nano Power.
The piezoelectric receiver generated totally different phases {of electrical} indicators relying on what a part of the ultrasound beam it interacted with. Probably the most environment friendly vitality switch occurred within the beam’s important lobe. In different phrases, bigger wasn’t essentially higher, although a bigger receiver would work together with extra of the ultrasound beam.
Based mostly on these circumstances, an oblong-shaped ultrasound transmitter and receiver was developed. This transmitter varieties a large important lobe at the focus, and the receiver matches the transmitted beam outputs vitality with excessive effectivity.
“The combination of a focused beam and a well-matched receiver allows oblong-shaped ultrasound transmitter and receiver to achieve significantly higher energy delivery compared to conventional ultrasound-based wireless power transfer systems,” Professor Chang says.
The system’s effectivity was examined each beneath water and thru 50mm of porcine tissue. The rectangular receiver was in a position to totally cost a battery by way of the tissue in 1.8 hours, which is effectively inside the vary required for industrial batteries.
“We believe that these findings will be a stepping stone for a significant advance in ultrasound-based wireless power transfer technology,” says Chang. “Its innovative design and demonstrated effectiveness hold tremendous potential for powering the next generation of deep implantable biomedical devices.”
Extra info:
Sungwoo Kang et al, Rectangular-shaped piezoelectric ultrasound vitality harvester for high-performance wi-fi energy charging, Nano Power (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2024.109618
Supplied by
Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Know-how (DGIST)
Quotation:
Improved ultrasound wi-fi charging for implantable biomedical gadgets (2024, Could 20)
retrieved 27 Could 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-05-ultrasound-wireless-implantable-biomedical-devices.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

