The worldwide chip scarcity was sparked in early 2020 as a result of COVID-19 pandemic. Provide points continued for over three years, impacting industries similar to shopper electronics and synthetic intelligence.
Almost each digital digital gadget at the moment is powered by semiconductors, which include silicon and are vital for creating built-in circuits, additionally known as microchips. And something that should compute or course of data, similar to smartphones, computer systems, and even on a regular basis home equipment, accommodates a chip.
Sadly, chips aren’t that simple to make — some specialists estimate that chips take so long as six months to supply. In consequence, chip makers mentioned ending the scarcity was troublesome “because it takes years to get new factories up and running,” based on the WSJ.
By July 2023, producers had ramped up manufacturing and their clients had adjusted to extra predictable chip provide. Enhancements in manufacturing capability and demand for shopper electronics cooling off have allowed industries like automotive to adapt and get better.
Nonetheless, export restrictions on key semiconductor supplies from China, similar to gallium and germanium, have fueled fears {that a} second chip scarcity is on the horizon.
What prompted the worldwide chip scarcity?
Like many issues, the chip scarcity was the results of larger demand for built-in circuits.
Even previous to the pandemic, the semiconductor provide chain was on shaky floor resulting from a collection of occasions, together with commerce wars between the U.S. and China and Japan and Korea, which impacted commodity pricing and distribution. As well as, pure disasters, similar to a drought in Taiwan and three plant fires in Japan between 2019 and 2021, contributed to uncooked materials shortages, based on Digital Merchandise & Know-how.
As soon as the automotive trade, a serious purchaser of semiconductors, started reducing chip orders in 2020, the semiconductor trade started shifting manufacturing to satisfy demand for different shopper purposes. Nonetheless, demand for vehicles picked up once more within the second half of 2020 as folks started avoiding public transportation. This exacerbated the availability and demand challenges additional.
SEE: Calculate your laptop {hardware}’s depreciation with this information from TechRepublic Premium.
The speedy acceleration of the Web of Issues was one other issue, and all of those mixed variables ” … eternally strikes semiconductors forward of oil because the world’s key commodity enter for development,” based on financial funding agency TS Lombard.
Some clients hoarded provides and purchased extra parts than they wanted in case provide dried up. For instance, corporations similar to Huawei stockpiled provides prematurely of U.S. tech bans on China in 2023. These actions additional exacerbated provide challenges with semiconductors.
The semiconductor market dimension
The semiconductor trade grows steadily and stays profitable. In 2021, McKinsey estimated gross sales to develop by greater than 20% to about $600 billion, with automotive, information storage, and wi-fi industries main the market (Determine A). The agency additionally predicts mixture annual development could common between 6% and eight% a yr by way of 2030.
Determine A
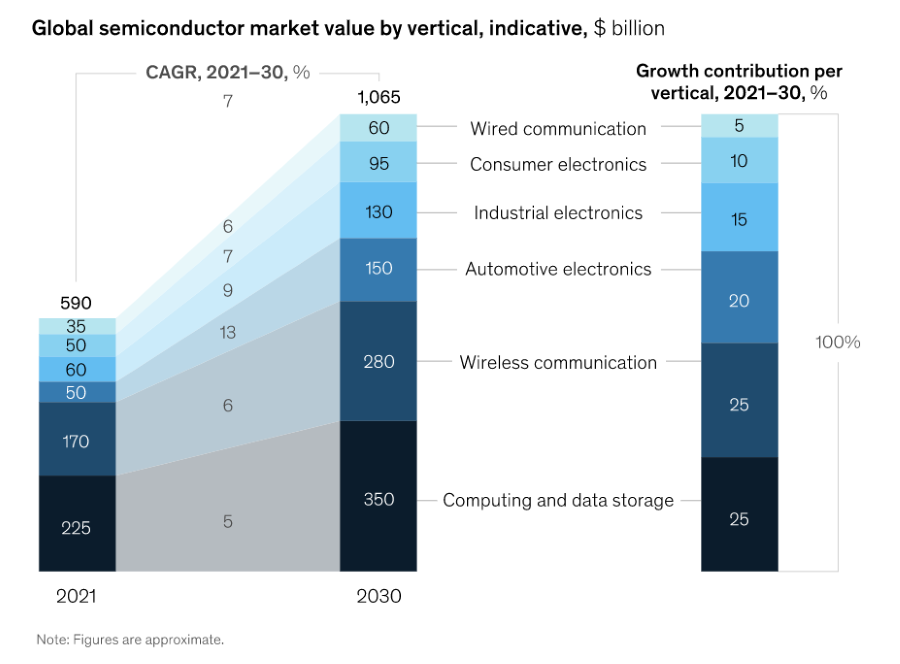
This may end in “a $1 trillion industry by the end of the decade, assuming average price increases of about 2 percent a year and a return to balanced supply and demand after the current volatility,” McKinsey mentioned.
The worldwide semiconductor market rose 6.8% in 2020 in comparison with 2019. It was projected to develop from $573.44 billion in 2022 to $1,380.79 billion by 2029, at a compound annual development charge of 12.2% within the forecast interval, 2022-2029, based on Fortune Enterprise Insights.
How industries have been impacted by the worldwide chip scarcity
Moreover the hard-hit automotive trade, the buyer electronics, industrial, smartphone, wired communications, and server and PC sectors have been impacted by the scarcity of chips.
Shopper electronics
Shopper electronics benefitted when the automotive trade started slashing automobile manufacturing early within the pandemic. Makers of laptops, TVs, smartphones, cameras, and gaming consoles ordered extra chips as a result of their merchandise closely rely on easy semiconductors:
- Home equipment similar to fridges, dishwashers, washing machines, and microwaves want semiconductors to regulate and regulate the circulation of electrical energy and make home equipment run extra effectively.
- Private computer systems have CPUs that act as their mind by executing directions and calculations.
- Cell units and smartphones use chips for communication, processing, reminiscence, and show — for instance, smartphones have a chip to connect with a mobile community, a chip to allow touchscreen enter and a chip that shops a consumer’s information.
The patron electronics trade needed to elevate costs within the face of shortages as demand exceeded provide and extra folks started working and going to high school remotely, requiring extra laptops, desktops, and different programs. Nonetheless, as a result of demand tends to be cyclical, the excessive demand for shopper electronics has tapered off.
Synthetic intelligence
AI and GPUs require a particular sort of chip to coach and deploy AI fashions as demand for AI computing energy grows, Chris Miller, a professor of historical past at Tufts College and writer of “Chip War: The Fight for the World’s Most Critical Technology,” instructed Market. These specialised and expensive GPUs are primarily made by NVIDIA at a producing plant in Taiwan, based on Miller.
NVIDIA and different GPU suppliers struggled to satisfy the skyrocketing demand for chips utilized in AI purposes, cloud computing, and machine studying resulting from provide chain disruptions through the world chip scarcity. This bottleneck delayed the event and deployment of AI applied sciences.
“As the economy slows, people are buying fewer smartphones, companies are spending less money updating their data centers,” Miller defined within the Market article. “But for the specific types of chips that are used for AI, there’s actually a boom and some shortages that are already becoming visible. And it seems like the demand for these types of chips is only set to grow.”
Why did restoration from the chip scarcity take so lengthy?
Provides of chips started to enhance in 2022, due partly to further capability with the slowdown in gross sales of PCs, smartphones, and shopper electronics. Foundries in Taiwan reallocated a few of this capability to the auto and industrial finish markets, based on JP Morgan.
Nonetheless, automakers more and more require chips with increased computing energy — particularly because the trade transitions to electrical and autonomous autos, that are considerably completely different from those utilized in PCs and smartphones.
Different roadblocks included tensions between the U.S. and China, which proceed to impression the worldwide provide chain. That is ” … spurring new authorities controls on gross sales of chips to China,” the world’s largest semiconductor market, the Semiconductor Trade Affiliation, famous in its State of the U.S. Semiconductor Trade report.
There have been different vital coverage challenges as properly, similar to the necessity to strengthen the U.S. semiconductor workforce by reforming the nation’s extremely expert immigration and STEM schooling programs. This may have elevated the variety of employees and helped include the expertise scarcity, based on the SIA.
The SIA added that macroeconomic headwinds and market cyclicality “caused a short-term downturn in sales.”
Demand stays unpredictable
There are some predictions that we are going to see one other chip scarcity resulting from a ” … mismatch between provide and demand that can’t be addressed rapidly both by chip producers … scaling up manufacturing or by markets by adapting to the chip manufacturing profile,” Rakesh Kumar wrote in Fortune. “The challenge of resolving the two isn’t going away — and may even grow in size.”
Semiconductor demand is unpredictable, Kumar defined. AI, electrical and autonomous autos, the Web of Issues, and 5G and 6G will drive future chip demand.
“Yet the exact nature, speed and magnitude of that increase in demand is still unknown,” Kumar wrote.
Semiconductor trade faces an absence of expert engineers
There’s one other concern: Whilst efforts are made to open up new semiconductor fabs, an absence of expert engineers could imply that lots of the jobs created gained’t be stuffed. In keeping with new information from the SIA, the trade is projected to develop by greater than 115,000 jobs by 2030, with 67,000 jobs liable to being unfilled (Determine B).
Determine B
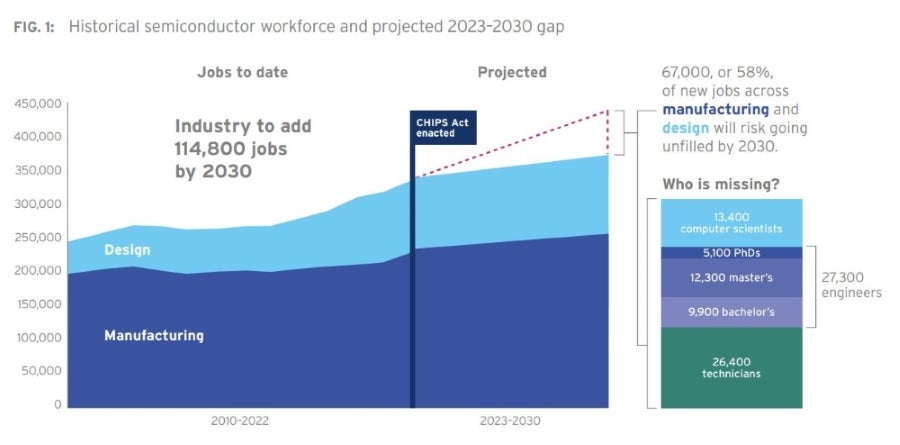
Increasing the availability of expert designers and different semiconductor professionals would require a sustained effort for a few years and even many years, mentioned Tony Chan Carusone, CTO of Alphawave Semi and professor {of electrical} engineering on the College of Toronto.
“This talent squeeze is not unique to the semiconductor industry but rather is going to affect the entire technology ecosystem,” Chan Carusone instructed TechRepublic. “For companies who are filling semiconductor roles, creating a more robust talent pipeline should be a top priority.”
The trade is ” … confronted with a difficult impediment resulting from the truth that chip know-how is just not simply seen or tinkered with, in contrast to software program,” Chan Carusone added. “This creates difficulty in attracting young tech professionals to pursue careers in hardware and semiconductors.”
Chan Carusone expressed hope that as one of the crucial essential subindustries inside tech, folks will think about a profession in semiconductors, which ” … is fast-paced, continuously evolving and will be a lot much less risky than a profession in software program.”
What efforts are being made to finish the chip scarcity?
Regardless of the challenges, the SIA says the long-term outlook for the semiconductor trade stays robust, with initiatives and insurance policies being made to extend semiconductor analysis and manufacturing globally.
International insurance policies push for semiconductor analysis and improvement
In 2022, the U.S. handed the CHIPS Act, which ” … has begun in earnest in 2023,” based on the SIA’s report. The CHIPS Act was enacted by the U.S. authorities to supply wanted semiconductor analysis investments and manufacturing incentives and to strengthen America’s financial system, nationwide safety, and provide chains.
The purpose of the $280 billion expenditure is to stop U.S. industries from falling prey to comparable semiconductor provide chain chaos sooner or later.
Since 2022, ” … corporations from all over the world have responded enthusiastically, saying dozens of latest semiconductor ecosystem tasks within the U.S. totaling properly over $200 billion in personal investments,” the SIA mentioned. “These projects will create tens of thousands of direct jobs in the semiconductor ecosystem and will support hundreds of thousands of additional jobs throughout the U.S. economy.”
In a push to bolster home semiconductor manufacturing abroad, the European Union has accredited the EU’s Chips Act, with the purpose of manufacturing 20% of the world’s semiconductors by 2030, Bloomberg reported. Nonetheless, in September 2024, the European Semiconductor Trade Affiliation known as for a “Chips Act 2.0,” which incorporates fewer export restrictions and would speed up the distribution of assist to assist the bloc obtain its purpose.
Semiconductor trade makes an effort to construct new crops
New crops at websites in Europe have already been introduced by chip makers, together with Intel and STMicroelectronics. Intel revealed it should make its chip manufacturing and foundry unit a stand-alone enterprise however stay beneath its company umbrella.
As of the beginning of 2024, IBM’s Altera will compete for enterprise like different exterior suppliers.
“It’s expected that this change will save as much as $3B this year and continue to generate savings to Intel’s bottom line going forward,” wrote trade analyst Jack Gold in a LinkedIn put up. “This is a major change to how Intel builds chips and we think it’s an important move that’s overdue.”
Intel mentioned the transfer will assist it obtain its acknowledged value financial savings purpose of greater than $8 billion to $10 billion by the top of 2025.
Semiconductor market launches to alleviate chip provide ache factors
In late September 2023, the Partstack Market launched as a semiconductor chip search platform for engineers, designers, and gear producers. Partstack goals to carry world semiconductor patrons and sellers collectively to rapidly find, purchase, or promote hundreds of thousands of hard-to-find semiconductor components from over 2,500 distinctive producers, based on its maker, semiconductor and electronics options supplier Partstack Company.
Partstack presents datasheets, guides for chip testing finest practices, and counterfeit element reporting options. It supplies a catalog of element pricing and availability information from world suppliers, the corporate mentioned.
Will there be one other world chip scarcity?
The preliminary outlook after the chip scarcity eased was optimistic. IEEE predicted the availability to develop ” … from older chip fabs and foundries working processes removed from the leading edge and on comparatively small silicon wafers.”
As well as, IEEE estimated that greater than 40 corporations would enhance capability by greater than 750,000 wafers monthly by the top of 2022. Intel, TSMC, Texas Devices, and Samsung — the world’s largest reminiscence chipmaker — all introduced plans to construct fabs within the U.S.
Regardless of this development, analysis from Omdia discovered that income from the semiconductor market declined by 9% in 2023 over the earlier yr. This was as a result of demand for shopper units softening in a weakened financial system, however the chip provide continued to extend.
There are additionally ” … a number of wild playing cards that might trigger extra disruption, similar to the worldwide financial system, geopolitical tensions, and the scarcity of kit for manufacturing bleeding-edge chips,” noticed administration consulting agency Bain & Co.
Nonetheless, the most important indicator of a future chip scarcity is the coverage modifications in China. In July 2023, the nation’s Ministry of Commerce introduced it will implement export controls on gallium and germanium-related objects “to safeguard national security and interests.” There’s hypothesis that the transfer got here in retaliation to export controls on the sale of semiconductors to China from the U.S. imposed in October 2022.
However the U.S. is just not the one nation that has cooled off buying and selling with China, because the Netherlands and Japan additionally collectively agreed to impose export controls on chipmaking kits in January 2023. The U.Ok. additionally blocked nearly all of license purposes for corporations searching for to export semiconductor know-how to China in 2023.
China’s restrictions have been enforced in August 2023, and based on information from the Monetary Instances, the price of the minerals has nearly doubled within the yr since. The nation produces 98% of the world’s provide of gallium and 54% of germanium, and the FT discovered that exports dropped by 12,000 kg and 14,359 kg, respectively, from the primary half of 2023 to the second.
“The United States is heavily reliant on imports for both of these critical minerals, especially from China, given its dominant role as a major producer and supplier of both products,” based on the U.S. Worldwide Commerce Fee.
The long-term outlook is unsure. Easing off on the West’s restrictions may assist stop a second world chip scarcity, however doing so would reinstate issues about China’s “ability to both purchase and manufacture certain high-end chips used in military application,” cited by the U.S. Division of Commerce.
However seemingly the other has occurred, because the U.S. rolled out a collection of latest chip-related export controls on China in September 2024.
“Assuming the global situation and US-China relationship stays as it is, then I don’t see any motivation for China to relax the export controls,” an worker at a big shopper of semiconductor supplies instructed the FT.
SEE: Take a look at all of TechRepublic’s cheat sheets and sensible individual’s guides.
