Li-ion batteries can current main hazards, with the notion of security based mostly on slender standards. A meta-analysis of thermal runaway fuel emissions by Sheffield researchers, printed within the Journal of Power Storage improves understanding and highlights the necessity for a broader evaluation of dangers.
A group from the Division of Chemical and Organic Engineering, led by Professor Sol Brown, performed an in depth meta-analysis of 60 papers in an effort to perceive extra in regards to the gases launched by lithium-ion batteries throughout thermal runaway (overheating).
The principle purpose of the assessment was to see how completely different battery options affected the quantity and sort of fuel launched, reminiscent of battery design and the way charged it’s, and to see if they might uncover what kind of battery is the least hazardous when it comes to hearth and explosions.
Professor Sol Brown, Professor of Course of and Power Programs, stated, “With the rise of electrical car gross sales and manufacturing, there’s a concern that we wouldn’t have a powerful understanding of the hazards they pose the place they fail and ignite.
“Unlike gasoline and diesel fires, which have been the subject of ample research, Li-ion battery fires are comparatively understudied. This restricts our ability to effectively deal with them if they occur. To address this gap, the meta-analysis we have undertaken highlights some key findings and makes recommendations for further research to improve battery safety in the future.”
When abused, lithium-ion batteries overheat and may catch hearth. Additionally throughout this course of is the discharge of gases which might explode, and have the potential to trigger severe harm. Additional, among the gases launched, reminiscent of carbon monoxide and hydrogen fluoride, are toxic and current a toxicity hazard.
Nevertheless, past these broad traits, the findings of the analysis into fuel emissions throughout thermal runway occasions usually are not clearly understood and should be in contrast in opposition to one another.
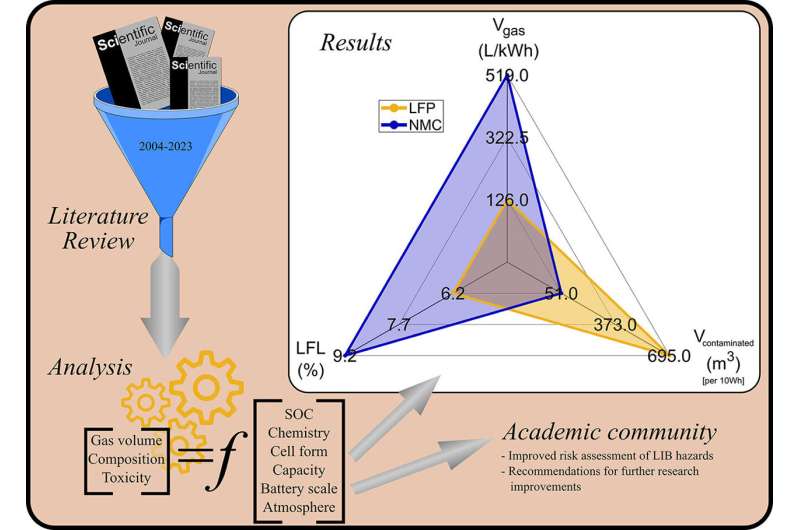
Many of the papers reviewed targeted on lithium ion phosphate (LFP) and lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC) batteries—each generally utilized in EVs.
Key findings:
- The whole quantity of fuel a battery releases will increase because the battery will get larger however the particular gases produced don’t change.
- The form of the battery issues—prismatic cells launch extra fuel than pouch with cylindrical releasing the least.
- NMC batteries launch extra fuel than LFP however LFP batteries are considerably extra poisonous
- Battery cost impacts toxicity—for NMC batteries the contaminated quantity doubles from 0% to 100% cost whereas for LFP it halves.
- LFP batteries produce extra hydrogen whereas NMC produce extra carbon monoxide. Researchers checked out one thing known as the Decrease Flammable Restrict (LFL) to find out how doubtless the fuel is to catch hearth. The decrease the LFL the simpler it’s for the fuel to ignite. In an inert ambiance the LFL ranges are for LFP 6.2% and NMC 7.9% so LFP batteries current a better flammability hazard.
The work within the paper goals to be a vital useful resource for the battery group to assist the chance evaluation of lithium-ion battery thermal runaway hearth, explosion and toxicity hazards.
The paper consists of a lot of suggestions in order that vital enhancements in analysis will be made to advance the understanding of lithium-ion off-gas additional, together with:
- Extra reporting on the fabric make-up of electrodes and the composition of the electrolytes inside NMC batteries. It will assist us higher perceive if and the way they have an effect on the gases launched.
- With the intention to get extra correct comparisons between excessive power LFP and NMC batteries, extra testing ought to be achieved on a wider vary of LFP pouch and prismatic cells (10–100 Ah).
- Testing bigger battery programs—present analysis focuses on single battery cells, however in real-world functions a number of cells are related collectively, so it might be useful to see how hazards scale with battery measurement.
- Measuring fuel launched at completely different cost ranges—to date research have solely checked out totally charged batteries. It will be helpful to see how toxicity and flammability of fuel modifications at completely different cost ranges, particularly when the battery is overcharged
- Future experiments ought to document how a lot and the kind of electrolyte that’s ejected as a vapor, as this may assist assess further hearth dangers.
Extra info:
Peter J. Bugryniec et al, Assessment of fuel emissions from lithium-ion battery thermal runaway failure — Contemplating poisonous and flammable compounds, Journal of Power Storage (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2024.111288
College of Sheffield
Quotation:
Meta-analysis paves the best way for safer batteries with diminished hearth and toxicity dangers (2024, September 5)
retrieved 5 September 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-09-meta-analysis-paves-safer-batteries.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.

