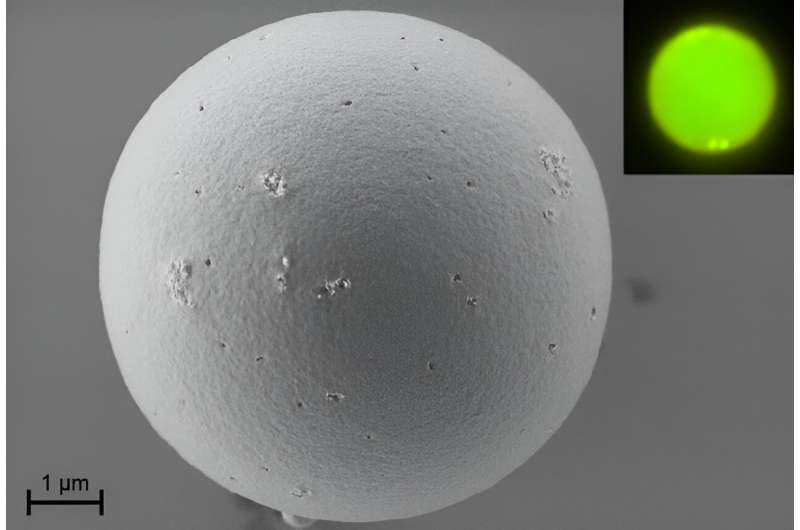
Researchers at IMDEA Nanociencia have fabricated top quality microspheres from conjugated natural polymer blends with glorious lasing properties. The laser emission of the microspheres has the very best high quality issue reported up to now, Q>18,000.
Dielectric optical microresonators confine and focus mild in a tiny round path as a result of a number of close to whole inner reflections on the curved dielectric-air interface, the place mild interferes constructively for sure wavelengths. These microresonators supply the likelihood to realize management of sunshine confinement and propagation by exact adjustment of their form, measurement and refractive index.
Amongst them, spherical resonators are notably fascinating as a result of their excessive Q components (ratio of the resonance frequency over its bandwidth) of the corresponding Mie resonances, or “whispering gallery modes.”
The Q issue is in essence a measure of how properly mild could be trapped within the microsphere over time and excessive Q components correspond to slender lasing linewidths, a desired characteristic when designing laser functions.
The slender resonances allow functions within the optical sensing subject, together with gadgets with excessive sensitivity to small bodily or chemical variations within the optical close to subject of the resonators. Additionally, excessive Q components pave the best way for functions within the subject of amplified spontaneous emission and lasing of microspheres made with luminescent supplies.
To this point, microlasers primarily based on conjugated polymers have been reported with typical Q components round 1,000. Conjugated polymers have emerged as glorious natural laser supplies for his or her excellent optoelectrical properties and facile processability.
Amongst all resonator geometries, microspheres manufactured from conjugated polymers mix massive optical absorption with excessive photoluminescence quantum yield, affording a rise of brightness with respect to industrial dye-doped microspheres beneath the identical photoexcitation circumstances.
Researchers at IMDEA Nanociencia institute (Madrid, Spain), led by Dr. Reinhold Wannemacher and Dr. Juan Cabanillas, have now reported microspheres primarily based on conjugated polymer blends exhibiting lasing with the very best high quality issue reported up to now, Q> 18,000.
The reported low lasing thresholds are primarily based on the vitality switch (Förster Resonant Power Switch, FRET) between the polymer constituents of the blends, a mechanism that reduces residual absorption on the lasing wavelength. Such low thresholds are promising for the event of microlasers which could be pumped by low-cost laser diodes.
The outcomes have been printed in Superior Optical Supplies.
Collectively, low thresholds and slender lasing linewidths allow ultrasensitive detection of variations of bodily parameters (pH, temperature) in addition to chemical composition of the atmosphere of the microspheres and, within the case of microspheres with surfaces functionalized by particular natural teams, ultra-sensitive and extremely particular detection of biomolecules.
The latter is extremely related for the event of transportable and low value biodetectors, which might allow fast prognosis of illnesses at factors of care.
Extra data:
Jorge González Sierra et al, Excessive Q Extremely‐Low Threshold Lasing in Conjugated Polymer Mix Microspheres Promoted by FRET, Superior Optical Supplies (2024). DOI: 10.1002/adom.202400161
Offered by
IMDEA Nanociencia
Quotation:
Natural polymer mix microspheres exhibit ultra-low threshold lasing with highest reported high quality issue (2024, July 22)
retrieved 22 July 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-07-polymer-blend-microspheres-ultra-threshold.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

