Roads are the spine of our society and financial system, taking individuals and items throughout distances lengthy and quick. They’re a staple of the constructed surroundings, taking over almost 2.8 million lane-miles (or 4.6 million lane-kilometers) of the US’ floor space.
These identical roads have a substantial life-cycle environmental impression, having been related to over 75 megatons of greenhouse gases (GHG) every year over the previous three many years in the US. That’s equal to the emissions of a gasoline-powered passenger car touring over 190 billion miles, or circling the Earth greater than 7.5 million instances, every year.
By 2050, it’s estimated that pavement sector emissions will lower by 14% as a result of enhancements like cement clinker alternative, however it’s doable to extract a 65% discount by way of measures like investing in supplies and upkeep practices to make street networks stiffer and smoother, which means they require much less power to drive on.
As a sensible instance, take into account that in 2022, automobiles in the US collectively drove 3.2 trillion miles. If the typical floor roughness of all pavements had been improved by 1%, there can be 190 million tons of CO2 saved every year.
One of many challenges to reaching better GHG reductions is information shortage, making it troublesome for resolution makers to guage the environmental impression of roads throughout their entire life cycle, comprising the emissions related to the manufacturing of uncooked supplies to building, use, upkeep and restore, and at last demolition or decommissioning.
Information shortage and the complexity of calculation would make analyzing the life-cycle environmental impacts of pavements prohibitively costly, stopping knowledgeable choices on what supplies to make use of and how one can preserve them. In the present day’s world is certainly one of fast change, with shifting climate and site visitors patterns presenting new challenges for roads.
In a brand new paper printed in Assets, Conservation and Recycling, authored by a workforce of researchers from MIT Concrete Sustainability Hub (CSHub), a brand new streamlined framework is proposed to allow the life-cycle evaluation (LCA) of pavements with restricted information.
“Conducting pavement LCA is dear and labor-intensive, so many assessments simplify the method utilizing mounted values for enter parameters or solely concentrate on upfront emissions from supplies manufacturing and building. Nonetheless, conducting LCA with mounted enter values fails to account for uncertainties and variations, which can result in unreliable outcomes.
“In this novel streamlined framework, we embrace and control the uncertainty in pavement LCA. This helps understand the minimum amount of data required to achieve a robust decision” notes Haoran Li, a postdoc at CSHub and the examine’s lead writer.
By preserving the uncertainty beneath management, the CSHub workforce develops a structured information underspecification framework that prioritizes accumulating information on the elements which have the best affect over pavement’s life-cycle environmental impacts.
“Typically, multiple pavement stakeholders, like designers, materials engineers, contractors, etc., need to provide extensive input data for conducting an LCA and comparing the environmental impacts of different pavement types,” says Hessam AzariJafari, deputy director of the CSHub and a co-author on the examine.
“These individuals are involved at different stages of a pavement project and none of them will have the necessary inputs for conducting a pavement LCA.”
The proposed streamlined LCA framework reduces the general information assortment burden by as much as 85% with out compromising the robustness of the conclusion on the environmentally most well-liked pavement sort.
The CSHub workforce used the proposed framework to mannequin the life-cycle environmental impacts of a pavement in Boston that had a size of 1 mile, 4 lanes, and a design life—or “life expectancy”—of fifty years. The workforce modeled two totally different pavement designs: an asphalt pavement and a jointed plain concrete pavement.
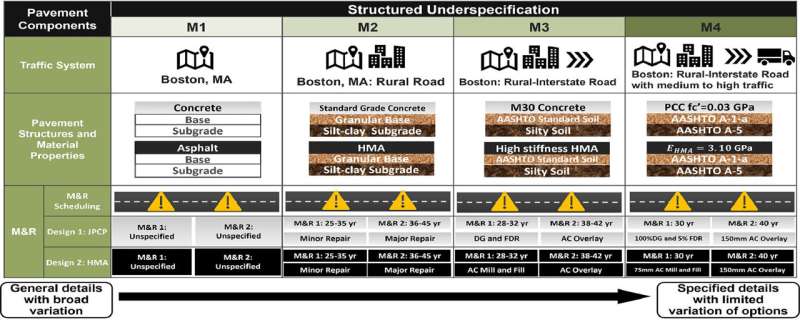
The MIT researchers then modeled 4 ranges of information specificity, M1 by way of M4, to grasp how they influenced the vary of life-cycle evaluation outcomes for the 2 totally different designs.
For instance, M1 signifies the best uncertainty as a result of restricted details about pavement situations, together with site visitors and supplies. M2 is usually used when the surroundings (city or rural) is outlined, however detailed data of fabric properties and future upkeep methods remains to be missing.
M3 presents an in depth description of pavement situations utilizing secondary information when discipline measurements usually are not out there. M4 offers the very best stage of information specificity, usually counting on first-hand data from designers.
MIT researchers discovered that the exact worth for greenhouse fuel emissions will differ from M1 to M4. Nonetheless, the proportionate emissions related to totally different parts of the life cycle stay related.
As an illustration, whatever the stage of information specificity, embodied emissions from building and upkeep and rehabilitation accounted for about half of the concrete pavement’s greenhouse fuel emissions. In distinction, the use section emissions for the asphalt pavement account for between 70% and 90% of the pavement’s life-cycle emissions.
The workforce discovered that, in Boston, combining an M2 stage of information specification with an M3 data of upkeep and rehabilitation produced a decision-making course of with 90% reliability.
To make this framework sensible and accessible, the MIT researchers are engaged on integrating the developed method into a web based life-cycle evaluation device. This device democratizes pavement LCA and empowers the chain stakeholders, similar to departments of transportation and metropolitan planning organizations, to determine decisions that result in the highest-performing, longest-lasting, and most environmentally pleasant pavements.
Extra data:
Haoran Li et al, Growth of a streamlined framework for probabilistic and comparative life cycle evaluation of street pavements, Assets, Conservation and Recycling (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2024.107802
Massachusetts Institute of Know-how
This story is republished courtesy of MIT Information (net.mit.edu/newsoffice/), a well-liked web site that covers information about MIT analysis, innovation and instructing.
Quotation:
New device empowers pavement life-cycle decision-making whereas decreasing information assortment burden (2024, August 12)
retrieved 12 August 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-08-tool-empowers-pavement-life-decision.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.

