SMU nanotechnology knowledgeable MinJun Kim and his crew have developed a quicker, extra exact approach to detect the properties and interactions of particular person proteins essential in speedy, correct, and real-time monitoring of virus-cell interactions. This might pave the best way for revolutionary medical therapies and developments to be created utilizing gene remedy—a way that makes use of innocent viruses to switch an individual’s genes to deal with or treatment illness.
Past that, this analysis is also used to detect and characterize different kinds of protein-protein interactions, doubtlessly resulting in the event of therapies that may regulate interactions inflicting antagonistic results within the physique, stated Kim, the Robert C. Womack Chair within the Lyle Faculty of Engineering at SMU and principal investigator of the BAST Lab.
A research printed within the journal Nanoscale exhibits that this tiny gadget Kim’s crew created precisely determines in real-time when two proteins that play a task in focused gene remedy—often called fibroblast development issue (FGF-1) and heparin—have bonded with one another.
And in contrast to the methods protein-protein interactions are detected now, this gadget solely wants a small pattern measurement to analyze the properties of particular person proteins and their advanced interactions, saving time and price for the evaluation.
Proteins are the workhorses that facilitate most organic processes in a cell. Usually, it is necessary for 2 or extra proteins to bind with one another—which means they’ve related with one another because of biochemical occasions—to hold out sure capabilities.
That is the case with proteins FGF-1 and heparin.
Collectively, these proteins have been proven to assist a innocent virus referred to as adeno-associated viruses (AAV)—which is the go-to car for gene remedy—latch on to the best cell receptors within the human physique.
Viral gene remedy makes use of viruses like AAVs as a approach to ship a wholesome copy of a gene into an individual to exchange or modify a disease-causing one. However the issue is that AAVs have a number of differing types, or serotypes, and every one has a pure choice to contaminate and thrive in particular tissue varieties, comparable to these serving the center or kidneys. That implies that for gene remedy to achieve success in unloading the virus’ cargo to its meant goal, the best serotype of AAV must bond with the proper cell receptors.
But, not sufficient is at the moment recognized about how this course of referred to as tropism works to make sure that.
“Thus, a better understanding of heparin and FGF-1 interactions will help us comprehend tropism for AAV gene therapy,” which, in flip, might make it potential to focus on new gene therapies for particular illnesses, Kim stated.
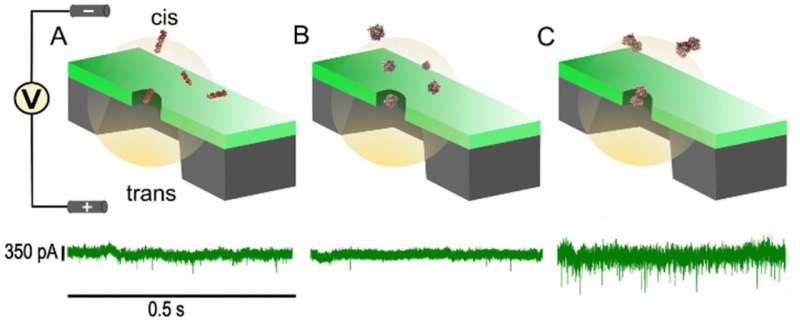
Kim’s crew created and examined a tool often called a solid-state nanopore, which might precisely inform when heparin and FGF-1 have bonded.
How the gadget works
Nanoparticles are too small to be seen to the bare eye—ranging in measurement from 1 to 100 nanometers (one billionth of a meter) in measurement. Nanomaterials can happen naturally and can be engineered to carry out particular capabilities, such because the supply of medicine to varied types of most cancers.
Every nanopore on this research was constructed from 12-nanometer-thick silicon nitride (SixNy) membranes, with a gap of roughly 17 nanometers in diameter drilled by way of it.
These so-called solid-state nanopores have been capable of inform when heparin bonded with FGF-1, as a result of Kim and his crew have calculated {the electrical} currents of three completely different situations: when solely heparin is current within the pattern; when solely FGF-1 is current; and when there may be an equal ratio of the 2 proteins.
How does the gadget know what {the electrical} present is?
Principally, a molecule from the pattern passes by way of a tiny gap within the gadget that separates two chambers containing electrolyte options. This results in fluctuations within the electrical present, which could be decoded to detect heparin-FGF-1 bonding.
Kim stated, “the findings of this research represent a preliminary experiment laying the groundwork for future endeavors.”
His final aim is to have the ability to use solid-state nanopores on two different proteins additionally recognized to be essential for focused gene remedy: the precise binding of the AAVs with cell floor receptors.
AAVs have a protein coat referred to as a capsid that surrounds their genetic info, which is what will get altered by gene therapists to introduce a brand new wholesome gene into an individual. It is just when capsids bind with cell receptors—one other protein discovered on the floor of cells—that the virus and cell are related and the virus’ cargo could be launched.
“The effectiveness of targeted gene therapy depends on the affinity between virus capsid and cell surface receptors,” Kim defined.
Kim desires to have the ability to use solid-state nanopores to measure that, making it clearer when a virus has efficiently delivered its cargo into an individual. That is as a result of a key barrier to utilizing viral gene remedy is that the quantity of genetic materials transmitted by AAV cannot be measured, doubtlessly resulting in overdosing or underdosing.
Along with making breakthroughs in gene remedy, lead research creator Navod Thyashan, a graduate analysis assistant at SMU’s BAST, famous that these nanopores might additionally set the stage for different new medical therapies to be developed. It may be used with different proteins recognized to have a excessive affinity for bonding with one another, permitting for therapies to doubtlessly regulate these interactions that trigger illnesses.
“Solid-state nanopores (SSNs) can be fabricated in sizes ranging from single digit nanometers in diameter to hundreds,” he stated. “Thus, SSNs can be used in most biomolecule sensing applications, as long as we choose the correct nanopore diameter for the proteins we are dealing with.”
Serving to Thyashan and Kim create the gadget have been Madhav L. Ghimire, the Dean’s Postdoctoral Fellow at SMU’s Moody Faculty of Graduate and Superior Research; and Sangyoup Lee, with the Bionic Analysis Middle for the Korea Institute of Science and Know-how.
Extra info:
Navod Thyashan et al, Exploring single-molecule interactions: heparin and FGF-1 proteins by way of solid-state nanopores, Nanoscale (2024). DOI: 10.1039/D4NR00274A
Supplied by
Southern Methodist College
Quotation:
New device to detect protein-protein interactions might result in promising avenues for gene remedy and different therapies (2024, June 13)
retrieved 13 June 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-06-tool-protein-interactions-avenues-gene.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

