A brand new molecular engineering method can exactly affect the event of organoids. Microbeads fabricated from particularly folded DNA are used to launch development components or different sign molecules contained in the tissue constructions. This offers rise to significantly extra complicated organoids that imitate the respective tissues a lot better and have a extra practical cell combine than earlier than.
An interdisciplinary analysis group from the Cluster of Excellence “3D Matter Made to Order” with researchers based mostly on the Middle for Organismal Research and the Middle for Molecular Biology of Heidelberg College, the college’s BioQuant Middle in addition to the Max Planck Institute for Medical Analysis in Heidelberg developed the method.
The analysis was printed within the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
Organoids are miniature, organ-like tissue constructions derived from stem cells. They’re utilized in primary analysis to achieve new insights into human improvement or to check the event of ailments.
“Until now it wasn’t possible to control the growth of such tissue structures from their interior,” states Dr. Cassian Afting, a Doctor Scientist on the Middle for Organismal Research (COS).
“Using the novel technique, we can now determine precisely when and where in the growing tissue key developmental signals are released,” emphasizes Tobias Walther, a biotechnologist and doctoral candidate on the Middle for Molecular Biology of Heidelberg College (ZMBH) and the Max Planck Institute for Medical Analysis in Heidelberg.
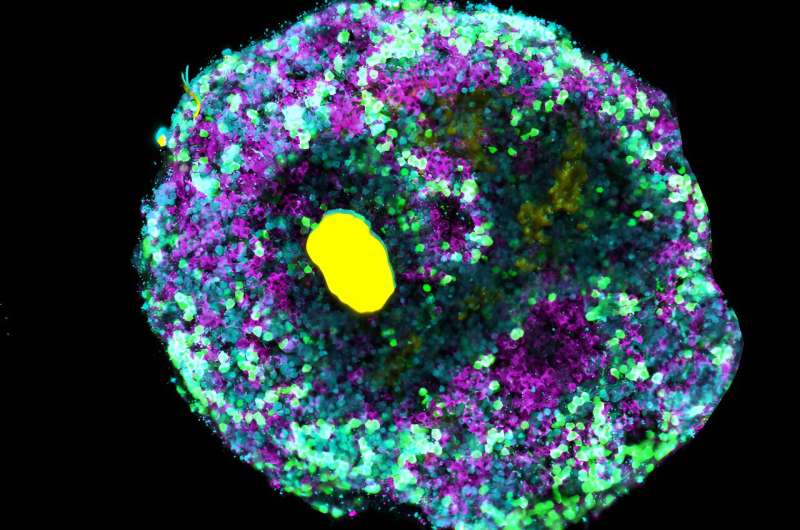
The interdisciplinary analysis group of biologists, physicians, physicists, and supplies scientists constructed microscopically small beads of DNA that may be “loaded” with proteins or different molecules. These microbeads are injected into the organoids and launch their cargo when uncovered to UV mild. This permits the discharge of development components or different sign molecules at any given time and placement throughout the growing tissue.
The researchers examined the method on retinal organoids of the Japanese rice fish medaka by exactly inserting microbeads loaded with a Wnt sign molecule into the tissue. For the primary time, they had been capable of induce retinal pigment epithelial cells—the outer layer of the retina—to kind adjoining to neural retinal tissue. Beforehand, including Wnt to the tradition media would induce pigment cells however suppress neural retina improvement.
“Thanks to the localized release of signaling molecules, we were able to achieve a more realistic mix of cell types, thereby more closely mimicking the natural cell composition of the fish eye than with conventional cell cultures,” explains Prof. Dr. Kerstin Göpfrich, a researcher within the subject of artificial biology on the ZMBH and the Max Planck Institute for Medical Analysis.
In response to the scientists, the DNA microbeads will be flexibly tailored to move many alternative sign molecules in numerous forms of cultivated tissue.
“This opens up new possibilities for engineering organoids with improved cellular complexity and organization,” states Prof. Dr. Joachim Wittbrodt, who directed the analysis work along with Prof. Göpfrich.
“More sophisticated organoid models could accelerate research on human development and disease and potentially lead to better organoid-based drug research,” states the Heidelberg developmental biologist, whose analysis group is positioned on the COS.
The brand new method for creating extra complicated organoids was developed within the Cluster of Excellence “3D Matter Made to Order,” which is operated collectively by Heidelberg College and the Karlsruhe Institute of Expertise.
Extra data:
Cassian Afting et al, DNA microbeads for spatio-temporally managed morphogen launch inside organoids, Nature Nanotechnology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01779-y
Offered by
Heidelberg College
Quotation:
New molecular engineering method permits for complicated organoids (2024, September 9)
retrieved 10 September 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-09-molecular-technique-complex-organoids.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.

