Griffith College researchers have developed modern, eco-friendly quantum supplies that may drive the transformation of methanol into ethylene glycol.
Ethylene glycol is a crucial chemical used to make polyester (together with PET) and antifreeze brokers, with a world manufacturing of over 35 million tons yearly with robust progress.
At the moment, it is primarily produced from petrochemicals by energy-intensive processes.
Methanol (CH3OH) will be produced sustainably from CO2, agricultural biomass waste, and plastic waste by varied strategies comparable to hydrogenation, catalytic partial oxidation, and fermentation. As a gasoline, methanol additionally serves as a round hydrogen service and a precursor for quite a few chemical substances.
Led by Professor Qin Li, from Griffith’s Queensland Micro- and Nanotechnology Middle, the workforce’s technique makes use of solar-driven photocatalysis to transform methanol into ethylene glycol beneath delicate situations. This course of makes use of daylight to drive chemical reactions, which minimizes waste and maximizes the usage of renewable vitality.
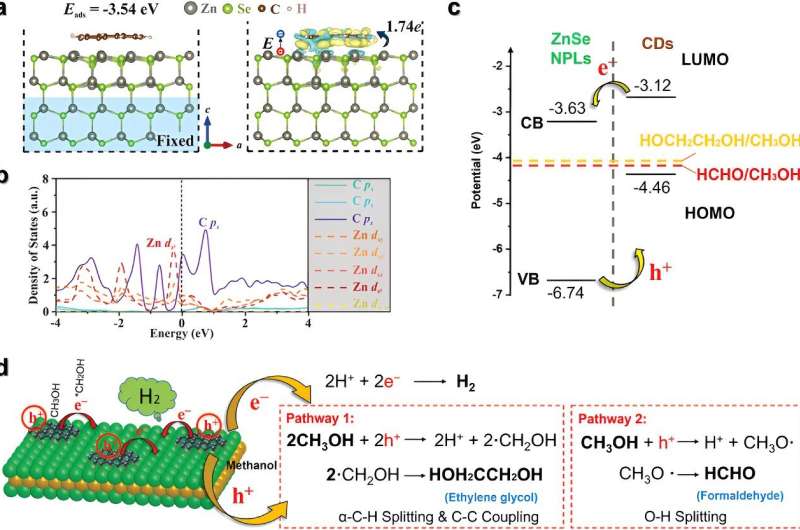
The research, “Colloidal Synthesis of Carbon Dot-ZnSe Nanoplatelet van der Waals Heterostructures for Boosting Photocatalytic Generation of Methanol-Storable Hydrogen,” has been printed within the journal Small.

Whereas earlier makes an attempt at this conversion have confronted challenges—comparable to the necessity for poisonous or valuable supplies—Professor Li and the analysis workforce have recognized a greener answer.
“Climate change is a major challenge facing humanity today,” Professor Li mentioned.
“To sort out this, we have to give attention to zero-emission energy era, low-emission manufacturing, and a round financial system. Methanol stands out as a vital chemical that hyperlinks these three methods.
“What we have created is a novel material that combines carbon quantum dots with zinc selenide quantum wells.”
“This combination significantly enhances the photocatalytic activity more than four times higher than using carbon quantum dots alone, demonstrating the effectiveness of the new material,” Lead creator Dr. Dechao Chen mentioned.
The strategy has additionally proven excessive photocurrent, indicating environment friendly cost switch inside the materials, essential for driving the specified chemical reactions.
Analyses confirmed the formation of ethylene glycol, and the byproduct of this response is inexperienced hydrogen. This discovery opens up new prospects for utilizing eco-friendly supplies in photocatalysis, paving the best way for sustainable chemical manufacturing.
As a brand new quantum materials, it additionally has the potential to result in additional developments in photocatalysis, sensing, and optoelectronics.
“Our research demonstrates a significant step towards green chemistry, showing how sustainable materials can be used to achieve important chemical transformations,” says Professor Qin Li. “This could transform methanol conversion and contribute significantly to emissions reduction.”
Extra info:
Dechao Chen et al, Colloidal Synthesis of Carbon Dot‐ZnSe Nanoplatelet van der Waals Heterostructures for Boosting Photocatalytic Era of Methanol‐Storable Hydrogen, Small (2024). DOI: 10.1002/smll.202402613
Journal info:
Small
Supplied by
Griffith College
Quotation:
New quantum materials places eco-friendly methanol conversion in attain (2024, June 17)
retrieved 26 June 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-06-quantum-material-eco-friendly-methanol.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.

