Schizophrenia is an advanced psychological well being dysfunction accompanied by a variety of signs resembling hallucinations, impaired cognitive means, and disorganized speech or conduct. It has been related to anomalies in neurotransmission as a result of imbalance of chemical neurotransmitters.
Present therapy methods in opposition to schizophrenia contain the administration of antipsychotic medicine, which might trigger opposed results and are related to a excessive threat of heart problems. Furthermore, in sufferers, response to therapeutic medicine is commonly insufficient because the blood-brain barrier (BBB), a protecting barrier of cells, strictly regulates the motion of ions and molecules into the mind.
To beat the hurdle of BBB and facilitate the transport of therapeutic medicine into mind tissue to deal with schizophrenia, researchers have explored the applicability of receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT) utilizing low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1).
This analysis was performed by a group led by Affiliate Professor Eijiro Miyako from Japan Superior Institute of Science and Know-how (JAIST), together with Prof. Yukio In the past from Hiroshima College, Prof. Shinsaku Nakagawa from Osaka College, Prof. Takatsugu Hirokawa from Tsukuba College, and Dr. Kotaro Sakamoto, Senior Principal Scientist at Ichimaru Pharcos Co., Ltd. Their research was printed within the JACS Au journal.
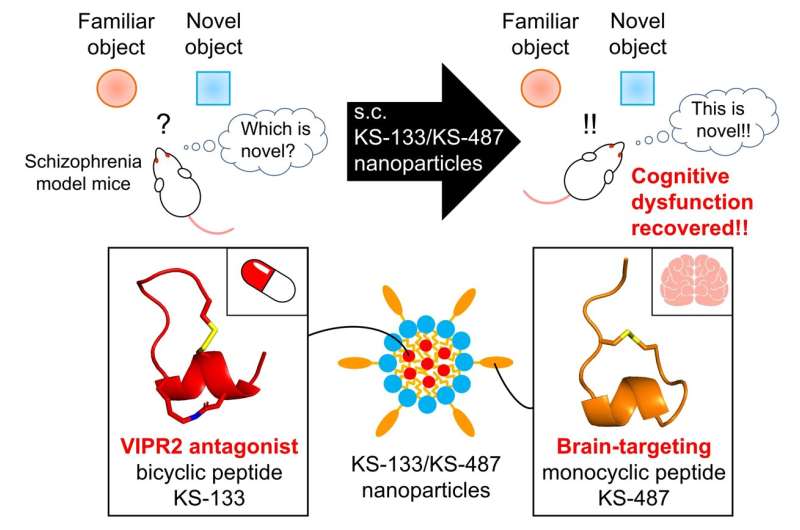
The researchers have been impressed by earlier findings displaying the interactions of vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 2 (VIPR2) gene duplication in schizophrenia and their very own discovery of a novel peptide, KS-133. The novel peptide, KS-133, has selective antagonist exercise with VIPR2, resulting in its downregulation. Nevertheless, the most important limitation related to KS-133 was its poor permeability throughout BBB.
To facilitate the efficient transport of KS-133 into the mind, they developed a brain-targeting peptide, KS-487, that might particularly bind to LRP1 and affect RMT. Lastly, the researchers developed a novel nanoparticle-based drug supply system (DDS) the place KS-133 peptide was encapsulated with KS-487 concentrating on peptide and studied its efficacy in treating schizophrenia.
The administration of peptide formulations through the DDS resulted within the efficient distribution of the drug within the brains of mice. Drug launch profiles assessed by pharmacokinetic evaluation confirmed the function of the brain-targeting peptide in transporting KS-133 into the mind. Moreover, the efficacy of DDS was evaluated in mice with induced schizophrenia by elevated activation of VIPR2. Mice handled with KS-133/KS-487 nanoparticles confirmed vital enchancment in cognitive features throughout novel object recognition checks, which may very well be attributed to the inhibition of VIPR2.
Explaining the real-life purposes and potential of their research, Dr. Miyako states, “Existing drugs only have mechanisms involving neurotransmitter modulation, and their therapeutic effects are limited, especially for cognitive dysfunction. Thus, our peptide formulation could be used as a novel drug to restore cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia.”
In abstract, this research by Dr. Miyako and co-researchers gives preclinical proof of a novel therapeutic technique for concentrating on VIPR2 that might enhance cognitive impairment in schizophrenia.
“Going ahead, we will extend our study to involve cells and animal models, as well as human clinical trials, to confirm the efficacy and safety of this peptide formulation and promote its development as a new treatment for schizophrenia within 5 years,” concludes Dr. Miyako, optimistic concerning the long-term implications of their research.
The researchers are hopeful that the invention and growth of novel DDS using bio-compatible peptides revolutionizes the therapy panorama of schizophrenia.
Extra data:
Kotaro Sakamoto et al, Cyclic Peptides KS-133 and KS-487 Multifunctionalized Nanoparticles Allow Environment friendly Mind Focusing on for Treating Schizophrenia, JACS Au (2024). DOI: 10.1021/jacsau.4c00311
Offered by
Japan Superior Institute of Science and Know-how
Quotation:
Novel peptide formulation reveals promise of restoring cognitive decline in schizophrenia (2024, June 27)
retrieved 27 June 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-06-peptide-cognitive-decline-schizophrenia.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.

