Editor’s Word: The next is an article written for and revealed in DZone’s 2024 Development Report, Cloud Native: Championing Cloud Growth Throughout the SDLC.
Cloud native and observability are an integral a part of developer lives. Understanding their obligations inside observability at scale helps builders sort out the challenges they’re dealing with each day. There may be extra to observability than simply accumulating and storing information, and builders are important to surviving these challenges.
Observability Foundations
Gone are the times of monitoring a identified utility setting, debugging companies inside our growth tooling, and ready for brand new sources to deploy our code to. This has develop into dynamic, agile, and shortly out there with auto-scaling infrastructure within the remaining manufacturing deployment environments.
Builders at the moment are striving to look at every thing they’re creating, from growth to manufacturing, typically proudly owning their code for the complete lifecycle. The tooling from days of outdated, reminiscent of Nagios and HP OpenView, cannot sustain with continually altering cloud environments that comprise 1000’s of microservices. The infrastructure for cloud-native deployments is designed to dynamically scale as wanted, making it much more important for observability platforms to assist condense all that information noise to detect developments resulting in downtime earlier than they occur.
Splintering of Obligations in Observability
Cloud-native complexity not solely modified the developer world but additionally impacted how organizations are structured. The obligations of making, deploying, and managing cloud-native infrastructure have break up right into a sequence of latest organizational groups.
Builders are being tasked with extra than simply code creation and are anticipated to undertake extra hybrid roles inside a few of these new groups. Observability groups have been created to give attention to a particular side of the cloud-native ecosystem to supply their group a service inside the cloud infrastructure. In Desk 1, we are able to see the splintering of conventional roles in organizations into these groups with particular focuses.
Desk 1. Who’s who within the observability recreation
| Staff | Focus | maturity objectives |
|---|---|---|
| DevOps | Automation and optimization of the app growth lifecycle, together with post-launch fixes and updates | Early phases: developer productiveness |
| Platform engineering | Designing and constructing toolchains and workflows that allow self-service capabilities for builders | Early phases: developer maturity and productiveness increase |
| CloudOps | Gives organizations correct (cloud) useful resource administration, utilizing DevOps ideas and IT operations utilized to cloud-based architectures to hurry up enterprise processes | Later phases: cloud useful resource administration, prices, and enterprise agility |
| SRE | All-purpose position aiming to handle reliability for any sort of setting; a full-time job avoiding downtime and optimizing efficiency of all apps and supporting infrastructure, no matter whether or not it is cloud native | Early to late phases: on-call engineers making an attempt to scale back downtime |
| Central observability staff | Chargeable for defining observability requirements and practices, delivering key information to engineering groups, and managing tooling and observability information storage | Later phases, proudly owning:
|
To grasp how these groups work collectively, think about a big, mature, cloud native group that has all of the groups featured in Desk 1:
- The DevOps staff is the primary line for standardizing how code is created, managed, examined, up to date, and deployed. They work with toolchains and workflow offered by the platform engineering staff. DevOps advises on new tooling and/or workflows, creating steady enhancements to each.
- A CloudOps staff focuses on cloud useful resource administration and getting essentially the most out of the budgets spent on the cloud by the opposite groups.
- An SRE staff is on name to handle reliability, avoiding downtime for all supporting infrastructure within the group. They supply suggestions for all of the groups to enhance instruments, processes, and platforms.
- The overarching central observability staff units the observability requirements for all groups to stick to, delivering the suitable observability information to the suitable groups and managing tooling and information storage.
Why Observability Is Essential to Cloud Native
As we speak, cloud native utilization has seen such development that builders are overwhelmed by their huge obligations that transcend simply coding. The complexity launched by cloud-native environments implies that observability is turning into important to fixing lots of the challenges builders are dealing with.
Challenges
Rising cloud native complexity implies that builders are offering extra code quicker and passing extra rigorous testing to make sure that their functions work at cloud native scale. These challenges expanded the necessity for observability inside what was historically the builders’ coding setting. Not solely do they should present code and testing infrastructure for his or her functions, they’re additionally required to instrument that code in order that enterprise metrics will be monitored.
Over time, builders realized that absolutely automating metrics was overkill, with a lot of that information being pointless. This led builders to positive tune their instrumentation strategies and switch to guide instrumentation, the place solely the metrics they wanted have been collected.
One other problem arises when selections are made to combine current utility landscapes with new observability practices in a company. The time builders spend manually instrumenting current functions in order that they supply the wanted information to an observability platform is an typically ignored burden.
New observability instruments designed to assist with metrics, logs, and traces are launched to the event groups — resulting in extra challenges for builders. Typically, these instruments are mastered by few, resulting in siloed data, which leads to organizations paying premium costs for superior observability instruments solely to have them used as if one is participating in observability as a toy.
Lastly, when exploring the ingested information from our cloud infrastructure, the very first thing that turns into apparent is that we need not preserve every thing that’s being ingested. We’d like the power to have management over our telemetry information and discover out what’s unused by our observability groups.
There are some questions we have to reply about how we are able to:
- Determine ingested information not utilized in dashboards, alerting guidelines, nor touched in advert hoc queries by our observability groups
- Management telemetry information with aggregation and guidelines earlier than we put it into costly, longer-term storage
- Use solely telemetry information wanted to assist the monitoring of our utility panorama
Tackling the flood of cloud information in such a manner as to filter out the unused telemetry information, protecting solely that which is utilized for our observability wants, is essential to creating this information beneficial to the group.
Cloud Native at Scale
The usage of cloud-native infrastructure brings with it numerous flexibility, however when carried out at scale, the small complexities can develop into overwhelming. That is as a result of premise of cloud native the place we describe how our infrastructure needs to be arrange, how our functions and microservices needs to be deployed, and eventually, the way it mechanically scales when wanted. This strategy reduces our management over how our manufacturing infrastructure reacts to surges in buyer utilization of a company’s companies.
Empowering Builders
Empowering builders begins with platform engineering groups that concentrate on developer experiences. We create developer experiences in our group that deal with observability as a precedence, dedicating sources for making a telemetry technique from day one. On this tradition, we’re establishing growth groups for achievement with cloud infrastructure, utilizing observability alongside testing, steady integration, and steady deployment.
Builders are usually not solely proudly owning the code they ship however at the moment are inspired and empowered to create, check, and personal the telemetry information from their functions and microservices. It is a courageous new world the place they’re the house owners of their work, offering agility and consensus inside the varied groups engaged on cloud options.
Rising to the challenges of observability in a cloud native world is a hit metric for any group, they usually cannot afford to get it unsuitable. Observability must be entrance of thoughts with builders, thought of a first-class citizen of their every day workflows, and persistently serving to them with challenges they face.
Synthetic Intelligence and Observability
Synthetic intelligence (AI) has risen in reputation inside not solely developer tooling but additionally within the observability area. The appliance of AI in observability falls inside certainly one of two use circumstances:
- Monitoring machine studying (ML) options or massive language mannequin (LLM) programs
- Embedding AI into observability tooling itself as an assistant
The primary case is once you need to monitor particular AI workloads, reminiscent of ML or LLMs. They are often additional break up into two conditions that you just may need to monitor, the coaching platform and the manufacturing platform.
Coaching infrastructure and the method concerned will be approached identical to every other workload: easy-to-achieve monitoring utilizing instrumentation and current strategies, reminiscent of observing particular traces by an answer. This isn’t the entire monitoring course of that goes with these options, however out-of-the-box observability options are fairly able to supporting infrastructure and utility monitoring of those workloads.
The second case is when AI assistants, reminiscent of chatbots, are included within the observability tooling that builders are uncovered to. That is typically within the type of a code assistant, reminiscent of one which helps positive tune a dashboard or question our time sequence information advert hoc. Whereas these are good to have, organizations are very conscious of developer utilization when inputting queries that embrace proprietary or delicate information. It is vital to know that coaching these instruments may embrace utilizing proprietary information of their coaching units, and even the info builders enter, to additional practice the brokers for future question help.
Predicting the way forward for AI-assisted observability is just not going to be simple as organizations take into account their information certainly one of their high valued property and can proceed to guard its utilization exterior of their management to assist enhance tooling. To that finish, one course that may assist adoption is to have brokers educated solely on in-house information, however which means the coaching information is smaller than publicly out there brokers.
Cloud-Native Observability: The Developer Survival Sample
Whereas we spend numerous time on tooling as builders, all of us perceive that tooling is just not all the time the repair for the advanced issues we face. Observability isn’t any totally different, and whereas builders are sometimes uncovered to the mantra of metrics, logs, and traces for fixing their observability challenges, this isn’t the trail to comply with with out contemplating the massive image.
The quantity of information generated in cloud-native environments, particularly at scale, makes it not possible to proceed accumulating all information. This flood of information, the challenges that come up, and the shortcoming to sift by the knowledge to seek out the foundation causes of points turns into detrimental to the success of growth groups. It might be extra useful if builders have been supported with simply the correct amount of information, in simply the suitable kinds, and on the proper time to resolve points. One doesn’t thoughts observability if the answer to issues are discovered shortly, conditions are remediated quicker, and builders are glad with the outcomes. If that is carried out with one log line, two spans from a hint, and three metric labels, then that is all we need to see.
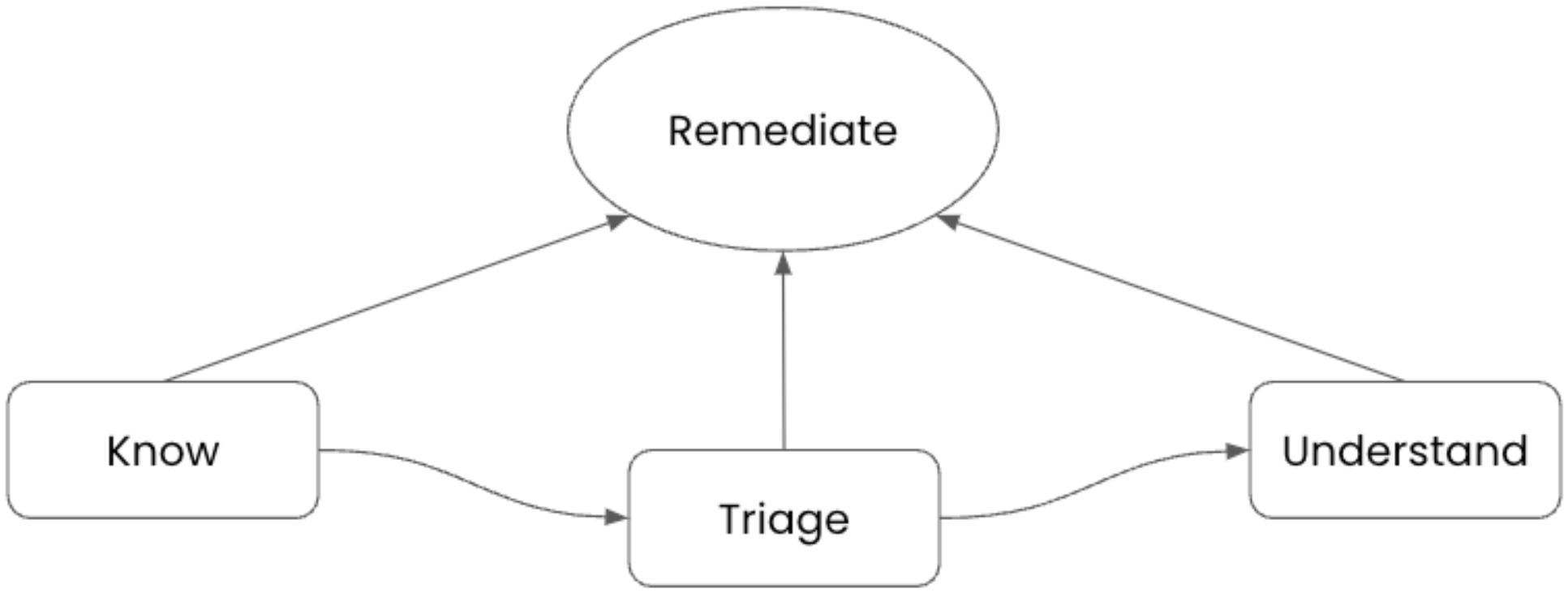
To do that, builders must know when points come up with their functions or companies, ideally earlier than it occurs. They begin troubleshooting with information that has been decided by their instrumented functions to succinctly level to areas inside the offending utility. Any tooling permits the developer who’s investigating to see dashboards reporting visible info that directs them to the issue and potential second it began. It’s essential for builders to have the ability to remediate the issue, possibly by rolling again a code change or deployment, so the appliance can proceed to assist buyer interactions. Determine 1 illustrates the trail taken by cloud native builders when fixing observability issues. The final step for any developer is to find out how points encountered will be prevented going ahead.
Determine 1. Observability sample
Conclusion
Observability is important for organizations to achieve a cloud native world. The splintering of obligations in observability, together with the challenges that cloud-native environments carry at scale, can’t be ignored. Understanding the challenges that builders face in cloud native organizations is essential to reaching observability happiness. Empowering builders, offering methods to sort out observability challenges, and understanding how the way forward for observability may look are the keys to dealing with observability in trendy cloud environments.
DZone Refcard sources:
That is an excerpt from DZone’s 2024 Development Report,
Cloud Native: Championing Cloud Growth Throughout the SDLC.Learn the Free Report

