A brand new research has found methods to scale back the toxicity of graphene oxide (GO), an ultra-thin sheet of nanomaterial derived from graphite, laying the groundwork to make use of it as a drug supply system.
Professor Khuloud Al-Jamal, who led the research, stated, “Researchers have been incredibly excited in the potential medical applications of graphene since experiments into the nanomaterial were recognized with the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2010. However, concerns around toxicity have remained a consistent obstacle.”
“In this study, we introduced chemical methods to make GO more biofriendly and unraveled the link between proteins in the corona and GO’s safety profile. Most importantly, we showed that in silico methods could accurately predict toxicity in mice offering ways to substitute the use of animals. I am proud of this cross-continent team effort between UK, Hong Kong, China and the U.S.,” stated Professor Al-Jamal, Professor of Drug Supply & Nanomedicine and Head of Medicines Improvement.
Graphene oxide (GO) is an ultra-thin sheet derived from graphite. It’s much like pencil lead however contains hooked up oxygen atoms, making it suitable with water. Its distinctive bodily and chemical properties imply it has a excessive capability for carrying antibiotics and anticancer medicine, amongst others, in addition to focusing on particular cells, making it a doubtlessly efficient drug supply system.
When GO enters the physique, it interacts with proteins present in organic fluids like plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. This interplay results in the formation of a hardened coating of proteins—in any other case often known as a protein corona—across the GO that influences the conduct and toxicity of the nanomaterial.
Due to this fact, to securely make the most of this drug supply system, important analysis is required to change the GO floor, or its supply methodology, and alleviate its poisonous impact contained in the physique.
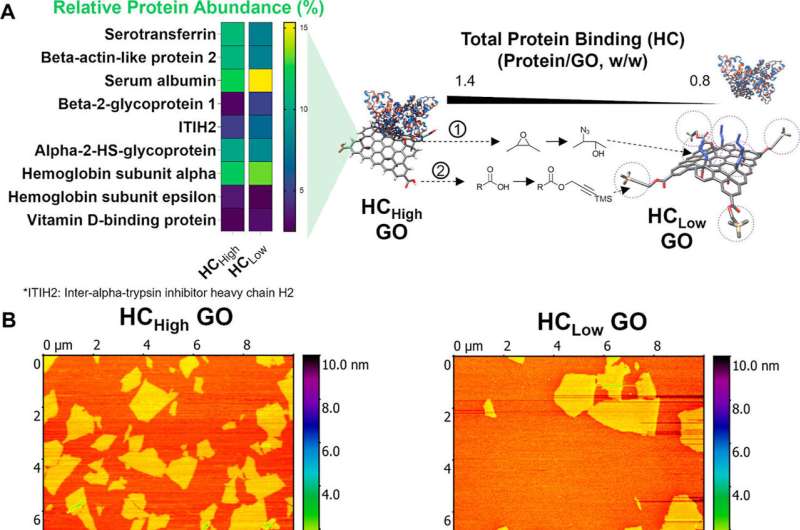
A brand new multidisciplinary research, printed in ACS Nano, was in a position to reveal the circumstances that trigger the corona to drive toxicity. Utilizing this data, the researchers subsequently investigated and recognized proteins within the corona that efficiently mitigated GO toxicity, creating potential for its use as a drug supply system and laying the groundwork for injectables and implants constructed from nanomaterials.
Two kinds of GO sheets with new chemical modifications have been examined to see how they bind to the corona protein, and their impression on the broader physique. Outcomes from mice fashions confirmed that sheets with a low protein coating brought on extra extreme harm to the liver and lungs, in addition to indicators of elevated molecular markers of irritation and blood toxicity. This was most obvious in mice fashions with regular, functioning immune programs.
Detailed evaluation of the findings allowed the researchers to determine constant patterns linking the protein coatings to their poisonous results in mice. They discovered that elevated amount of the corona led to diminished toxicity from the GO, with additional evaluation figuring out key proteins inside it that would additionally mitigate the toxicity of the nanomaterial.
This multidisciplinary strategy, comprising chemistry, 2D supplies, proteomics, mathematical modeling and animal analysis is a significant step ahead for the potential sensible utility of GO as a drug supply system and different nanomaterials.
Extra data:
Yue-ting Li et al, Graphene Oxide Nanosheets Toxicity in Mice Is Depending on Protein Corona Composition and Host Immunity, ACS Nano (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.4c08561
Supplied by
King’s Faculty London
Quotation:
Research finds protein reduces toxicity of graphene oxide for drug supply (2024, August 13)
retrieved 13 August 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-08-protein-toxicity-graphene-oxide-drug.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

