Researchers on the College of Kentucky have a greater understanding of the regulation of extracellular vesicles by oxidative stress and the way these vesicles unfold oxidative stress and will harm neurons. Extracellular vesicles are nanoparticles launched by all cell varieties that assist transport data between cells.
The research titled “Ceramide-mediated orchestration of oxidative stress response through filopodia-derived small extracellular vesicles” was lately printed within the Journal of Extracellular Vesicles.
“This study lays the groundwork to learn what’s happening during the exchange of extracellular vesicles between different cell types to then work toward understanding the significance of these processes in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease,” mentioned Erhard Bieberich, Ph.D., a professor within the Division of Physiology within the UK School of Medication. Bieberich is the principal investigator.
Bieberich’s analysis workforce centered on oxidative stress—an extra of oxygen radicals within the physique. This extra leads to harm to cells and tissues. Different research have proven this performs a job in lots of continual and degenerative situations.
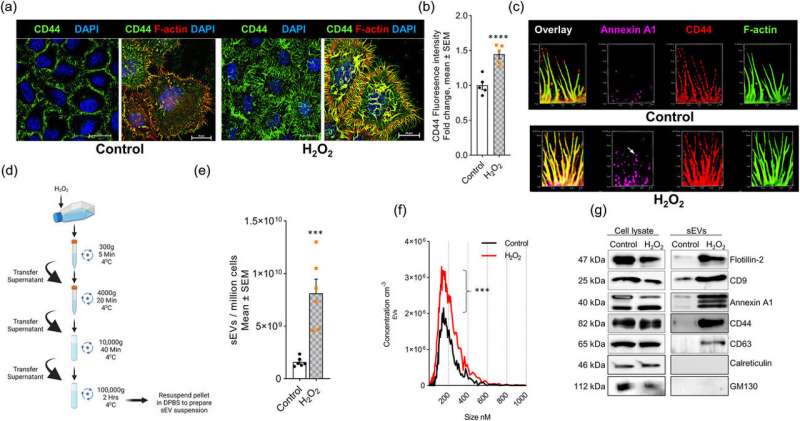
Researchers studied HeLa cells, that are so-called “immortal” cells for his or her distinctive capacity to constantly develop and divide within the lab. When uncovered to hydrogen peroxide, the cells shaped filopodia (finger-like projections of cell membranes) and secreted extracellular vesicles (tiny constructions launched from cell membranes).
“In our study, we investigated the function of ceramide, which is a type of fatty compound, in filopodia formation and extracellular vesicle secretion, both of which are induced by oxidative stress,” mentioned Bieberich.
“Using a novel metabolic labeling technique, we found that those two processes are controlled by two enzymes that generate ceramide at the plasma membrane,” mentioned Zainuddin Quadri, the primary creator of the research and a senior analysis affiliate within the Division of Physiology. “This leads to the release of ceramide-rich small extracellular vesicles from filopodia, which then target mitochondria and cause cell death.”
“Previous research focused on oxidative stress caused by the accumulation of amyloid in plaques or other proteins in neurons,” mentioned Bieberich.
“We discovered a novel mechanism by which oxidative stress can be spread through extracellular vesicles, which may propagate cell death even if neurons themselves are not directly exposed to harmful proteins such as amyloid.”
The 2 researchers mentioned the induction of cell dying was discovered significantly in neuronal cells, however plan to additional research the method in several types of cells.
Their findings counsel that concentrating on the interplay between the 2 enzymes could possibly be a possible therapeutic goal to forestall oxidative stress-induced cell dying.
This analysis was made attainable by the collaboration with two lipid biologists, Stefanka Spassieva, Ph.D., and Mariana Nikolova-Karakashian, Ph.D., within the Division of Physiology. They’re additionally co-authors on the publication.
Extra data:
Zainuddin Quadri et al, Ceramide‐mediated orchestration of oxidative stress response by means of filopodia‐derived small extracellular vesicles, Journal of Extracellular Vesicles (2024). DOI: 10.1002/jev2.12477
Supplied by
College of Kentucky
Quotation:
Research hyperlinks nanoparticles to oxidative stress and neuron dying (2024, July 23)
retrieved 23 July 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-07-links-nanoparticles-oxidative-stress-neuron.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.

