Versatile piezoelectric sensors are important to watch the motions of each people and humanoid robots. Nevertheless, current designs are both expensive or have restricted sensitivity.
In a current examine, researchers from Japan tackled these points by creating a novel piezoelectric composite materials made out of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers mixed with dopamine. Sensors made out of this materials confirmed vital efficiency and stability enhancements at a low price, promising developments in drugs, well being care, and robotics.
Their examine, which was led by Distinguished Professor Ick Soo Kim in affiliation with Junpeng Xiong, Ling Wang, Mayakrishnan Gopiraman, and Jian Shi, is revealed in Superior Fiber Supplies.
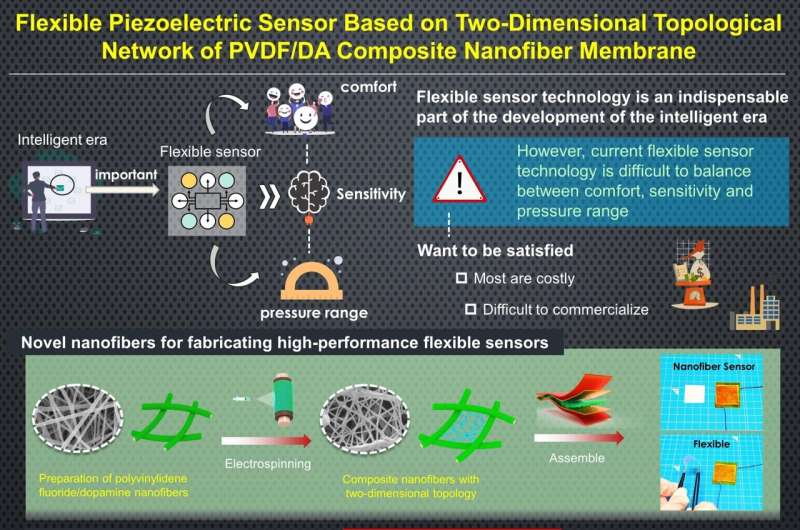
The world is accelerating quickly in the direction of the clever period—a stage in historical past marked by elevated automation and interconnectivity by leveraging applied sciences resembling synthetic intelligence and robotics. As a sometimes-overlooked foundational requirement on this transformation, sensors characterize a necessary interface between people, machines, and their atmosphere.
Nevertheless, now that robots have gotten extra agile and wearable electronics are now not confined to science fiction, conventional silicon-based sensors will not make the minimize in lots of functions. Thus, versatile sensors, which give higher consolation and better versatility, have turn out to be a really lively space of examine.
Piezoelectric sensors are significantly essential on this regard, as they’ll convert mechanical stress and stretching into {an electrical} sign. Regardless of quite a few promising approaches, there stays a scarcity of environmentally sustainable strategies for mass-producing versatile, high-performance piezoelectric sensors at a low price.
Towards this backdrop, a analysis workforce from Shinshu College, Japan, determined to step as much as the problem and enhance versatile piezoelectric sensor design utilizing a well-established manufacturing approach: electrospinning.
The proposed versatile sensor design entails the stepwise electrospinning of a composite 2D nanofiber membrane. First, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofibers with diameters on the order of 200 nm are spun, forming a robust uniform community that acts as the bottom for the piezoelectric sensor.
Then, ultrafine PVDF nanofibers with diameters smaller than 35 nm are spun onto the preexisting base. These fibers turn out to be robotically interweaved between the gaps of the bottom community, creating a specific 2D topology.
After characterization through experiments, simulations, and theoretical analyses, the researchers discovered that the ensuing composite PVDF community had enhanced beta crystal orientation.
By enhancing this polar section, which is chargeable for the piezoelectric impact noticed in PVDF supplies, the piezoelectric efficiency of the sensors was considerably improved. To extend the soundness of the fabric additional, the researchers launched dopamine (DA) through the electrospinning course of, which created a protecting core–shell construction.
“Sensor fabricated from using PVDF/DA composite membranes exhibited superb performance, including a wide response range of 1.5–40 N, high sensitivity of 7.29 V/N to weak forces in the range of 0–4 N, and excellent operational durability,” stated Kim.
These distinctive qualities had been demonstrated virtually utilizing wearable sensors to measure all kinds of human actions and actions. Extra particularly, the proposed sensors, when worn by a human, might produce an simply distinguishable voltage response to pure motions and physiological alerts. This included finger tapping, knee and elbow bending, foot stamping, and even talking and wrist pulses.
Given the potential low-cost mass manufacturing of those piezoelectric sensors, mixed with their use of environmentally pleasant natural supplies as a substitute of dangerous inorganics, this examine might have essential technological implications not just for well being monitoring and diagnostics, but additionally robotics.
“Despite the current challenges, humanoid robots are poised to play an increasingly integral role in the very near future. For instance, the well-known Tesla robot ‘Optimus’ can already mimic human motions and walk like a human,” added Kim.
“Considering high-tech sensors are currently being used to monitor robot motions, our proposed nanofiber-based superior piezoelectric sensors hold much potential not only for monitoring human movements, but also in the field of humanoid robotics.”
To make the adoption of those sensors simpler, the analysis workforce shall be specializing in enhancing the fabric’s electrical output properties in order that versatile digital elements might be pushed with out the necessity for an exterior energy supply.
Extra info:
Junpeng Xiong et al, Versatile Piezoelectric Sensor Primarily based on Two-Dimensional Topological Community of PVDF/DA Composite Nanofiber Membrane, Superior Fiber Supplies (2024). DOI: 10.1007/s42765-024-00415-7
Supplied by
Shinshu College
Quotation:
Research makes use of electrospun nanofibers to enhance versatile piezoelectric sensors (2024, June 12)
retrieved 13 June 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-06-electrospun-nanofibers-flexible-piezoelectric-sensors.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

