Researchers at Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa College report in Biosensors and Bioelectronics: X a novel strategy for detecting a specific biomolecule related to a number of illnesses. The outcomes present good sensitivity and selectivity, and will result in the event of a low-cost, fast detection system helpful in most cancers prognosis.
Human illnesses are sometimes the results of DNA transcriptions gone improper. Transcription refers back to the copying of elements of a DNA molecule—the ‘genetic code’—into an RNA molecule, which in flip is required for changing the encoded info into proteins. The latter play essential roles in numerous biochemical processes going down within the human physique.
One transcriptional modification mechanism is adenosine-to-inosine modifying, during which adenosine (certainly one of 4 RNA constructing blocks) is chemically modified, leading to an altered RNA molecule. The sort of modification is facilitated by catalyst proteins known as ADARs (adenosine deaminases appearing on RNA).
Three such ADARs have been recognized in people. Considered one of them, ADAR1, has been discovered to be extra plentiful within the presence of a number of sorts of continual illnesses, together with neurological issues and most cancers. ADAR1 is due to this fact thought of a biomarker—a ‘signature molecule’—for assessing a affected person’s situation and probabilities of survival.
Madhu Biyani from Kanazawa College and colleagues have now developed a brand new electrochemical biosensor for detecting ADAR1, providing a low-cost, fast software for measuring ADAR1 concentrations in cells. The detector is predicted to be helpful for monitoring most cancers development.
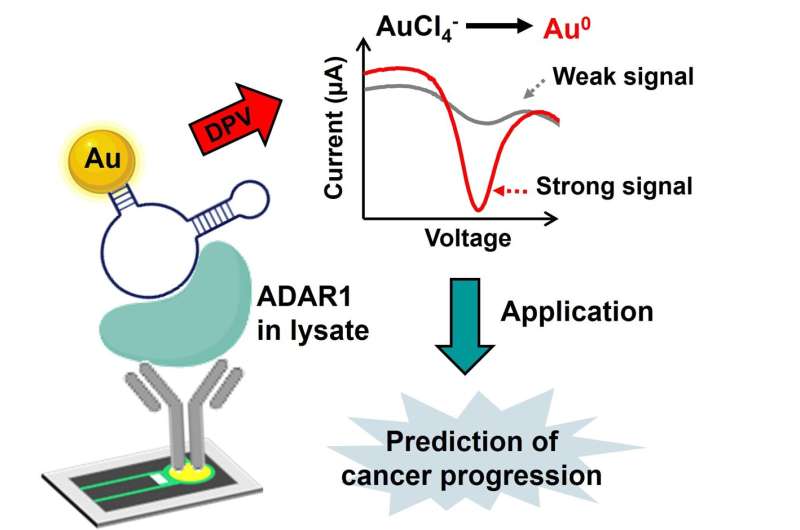
The process introduced by Biyani and colleagues is new in two methods. The primary is that it makes use of newly recognized aptamers as molecules that may acknowledge and seize ADAR1. Aptamers are molecules consisting of sequences of (artificial) DNA, RNA or different biomolecules that bind to a specific goal molecule, on this case ADAR1. The second novelty lies in using a field-deployable electrochemical sensor DEPSOR (BioSeeds Corp.), which has some great benefits of, other than being quick and non-expensive, requiring solely small samples.
As a way to discover the optimum aptamer—that’s, the one which chemically binds best to ADAR1—the researchers screened a big set of DNA sequences and narrowed it down to fifteen candidate aptamers. Every of those candidates was then examined in an electrochemical sensing platform: the quantity of ADAR1 is ‘sensed’ by means of chemical reactions that lead to {an electrical} present. The latter might be simply detected. The extra ADAR1 in a pattern, the upper the measured present.
The candidate aptamer ensuing within the highest electrochemical present, known as Apt38483, was then checked additional. Its electrochemical response to ‘false’ proteins was very low, confirming it to be the optimum aptamer by way of each sensitivity and selectivity.
The scientists then examined an Apt38483-based prototype system on diluted cell samples. They discovered that even in a 625-fold diluted pattern, ADAR1 may nonetheless be detected, highlighting the excessive sensitivity of the system.
The electrochemical biosensor developed by Biyani and colleagues for the detection of ADAR1 in cell samples is a promising platform for monitoring most cancers development in medical samples. The scientists stated, “In the future, it will be promising to evaluate the system for the identification of low to high levels of ADAR1 expression in a cancer cell line sample for clinical prognosis.”
Background: Electrochemical biosensors
Electrochemical biosensors are units that convert organic info, such because the presence of a specific molecule (known as the analyte), right into a measurable sign. Primarily, biosensors encompass a bioreceptor, an interface and a transducer factor. The bioreceptor binds to the analyte on the interface, which leads to a sign that’s picked up and transformed by the transducer into an electrical sign.
The electrical sign is processed by means of a pc; for instance, the sign might be transformed into an analyte focus studying. Electrochemical biosensors are usually sturdy, low-cost and simple to miniaturize.
Madhu Biyani from Kanazawa College and colleagues have now developed an electrochemical biosensor for the detection of ADAR1, an RNA-editing enzyme related to most cancers development. They recognized a specific biomolecule because the optimum bioreceptor, exhibiting good sensitivity and selectivity for ADAR1. The developed system is predicted to be helpful for monitoring most cancers development.
Extra info:
Madhu Biyani et al, A novel aptamer-antibody sandwich electrochemical sensor for detecting ADAR1 in complicated organic samples, Biosensors and Bioelectronics: X (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.biosx.2024.100491
Offered by
Nano Life Science Institute (NanoLSI), Kanazawa College
Quotation:
Researchers develop new electrochemical biosensor for most cancers prognosis (2024, June 13)
retrieved 13 June 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-06-electrochemical-biosensor-cancer-prognosis.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

