Scientists at Tub, have launched a breakthrough carbon-based sensor for detecting lactic acid ranges in saliva—avoiding the necessity for {an electrical} energy supply.
The researchers, working in collaboration with industrial associate, Built-in Graphene, have created a brand new sort of chemosensor (demonstrated for lactic acid sensing) which capabilities with electrical energy however with out the necessity for reference electrodes or battery energy. The brand new design doubtlessly affords decrease price, higher shelf-life, and ease of miniaturization in comparison with enzyme-based sensors.
The sensor was confirmed to detect lactic acid, a by-product generated by the physique when it metabolizes carbohydrates or glucose for gasoline, for instance, throughout train. Excessive ranges of lactic acid are linked with greater dangers of falling unconscious or right into a coma and main organ failure.
This opens up the chance for an easy-to-use sensor for use in distant places, comparable to an athletics monitor, with out the necessity for electricity-powered sensing gear.
At the moment, lactic acid is commonly measured with an enzyme check, which has a restricted shelf life and requires battery powered sensing gear. The brand new sort of chemosensor, detailed in a paper printed in ACS Sensors, as an alternative measures lactic acid with a chemical methodology utilizing a graphene foam electrode floor.
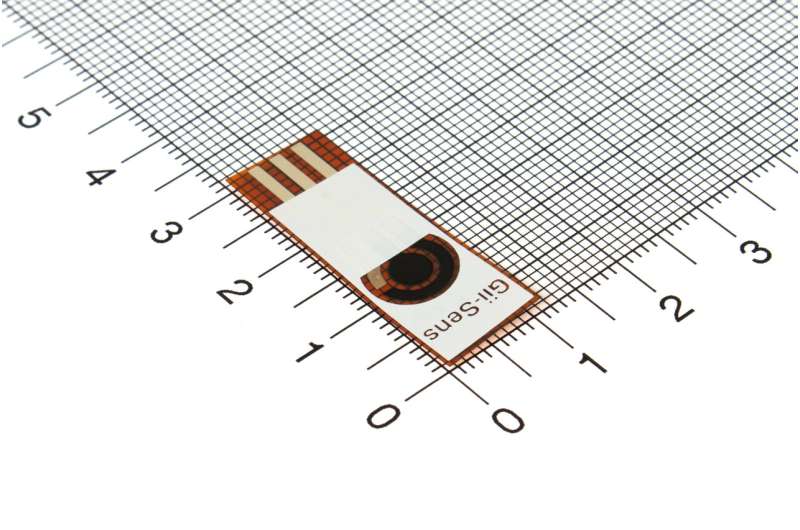
Referenced as “Graphene Foam” within the paper, Gii-Sens, the expertise underpinning the chemosensor, is an electrode produced by Built-in Graphene. Gii-Sens incorporates Gii, a pure, porous, 3D carbon nanostructure that delivers low price and avoids using unsustainable noble metals like gold.
When lactate binds to the sensor, it causes a change within the electrical sign—or quantum capacitance—of the carbon foam. The froth subsequently detects low ranges of lactic acid with out consuming it by measuring adjustments within the electrical charging of Gii, permitting the monitoring of adjustments in ranges. As it’s a chemical fairly than an enzyme-based sensor, it has a doubtlessly decrease price, higher shelf-life, and ease of miniaturization.
Professor Frank Marken, lead writer of the examine on the College of Tub, mentioned, “Just as your contactless credit card doesn’t need an external power source to work because the proximity of the card reader is enough to power it—in a similar way, this sensor could create a small, measurable electrical current when lactate binds to it.”
“This sensor, using Gii-Sens technology, addresses some of the main limitations with non-wireless current lactic acid enzyme tests,” mentioned Professor Marken, “It will allow for a more simply operated sensor—opening up the potential for more regular, less invasive and more reliable tracking of lactic acid, even during athlete performance.”
Lactic acid assessments have numerous vital purposes. In skilled sports activities, lactic acid is examined to evaluate the athlete’s response to completely different intensities and coaching regimes. By wirelessly monitoring and subsequently bettering the physique’s skill to move and make the most of lactate, athletes goal to enhance their endurance and restoration.
Additionally it is utilized in medical care to trace coronary heart circumstances like myocardial infarctions, atrial fibrillation, and atherosclerosis. That is helpful as elevated lactic acid ranges can scale back the center and blood vessel’s skill to contract, impacting the hemodynamics for normal perform.
Jean-Christophe Granier, Chief Government Officer of Built-in Graphene, commented, “This growth is one other clear use case of Gii-Sens being built-in into sensing merchandise and providing versatile applicability.
“The researcher’s test results using our Gii-Sens electrode opens up the possibility of more accessible and reliable health monitoring in remote environments and we look forward to putting our highly sensitive Gii-Sens electrode at the heart of more groundbreaking innovations in the point of care diagnostics market.”
Extra data:
Simon M. Wikeley et al, Pyrene-Appended Boronic Acids on Graphene Foam Electrodes Present Quantum Capacitance-Primarily based Molecular Sensors for Lactate, ACS Sensors (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acssensors.4c00027
Offered by
College of Tub
Quotation:
Scientists develop new battery-free lactic acid sensor (2024, Might 22)
retrieved 25 Might 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-05-scientists-battery-free-lactic-acid.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

