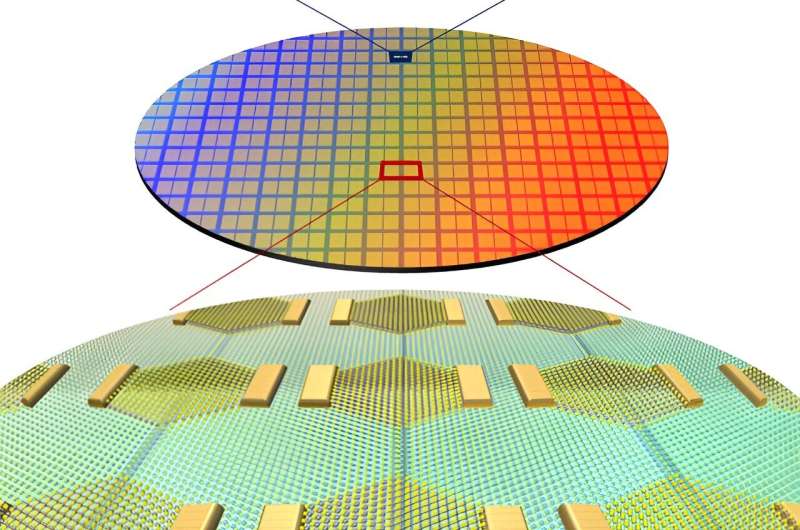
A analysis crew led by Director Jo Moon-Ho of the Middle for Van der Waals Quantum Solids inside the Institute for Fundamental Science (IBS) has carried out a novel technique to attain epitaxial development of 1D metallic supplies with a width of lower than 1 nm. The group utilized this course of to develop a brand new construction for 2D semiconductor logic circuits. Notably, they used the 1D metals as a gate electrode of the ultra-miniaturized transistor.
This analysis seems in Nature Nanotechnology.
Built-in gadgets primarily based on two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors, which exhibit wonderful properties even on the final restrict of fabric thickness right down to the atomic scale, are a significant focus of fundamental and utilized analysis worldwide. Nonetheless, realizing such ultra-miniaturized transistor gadgets that may management the electron motion inside a couple of nanometers, not to mention creating the manufacturing course of for these built-in circuits, has been met with vital technical challenges.
The diploma of integration in semiconductor gadgets is set by the width and management effectivity of the gate electrode, which controls the stream of electrons within the transistor. In typical semiconductor fabrication processes, decreasing the gate size under a couple of nanometers is unimaginable because of the limitations of lithography decision.
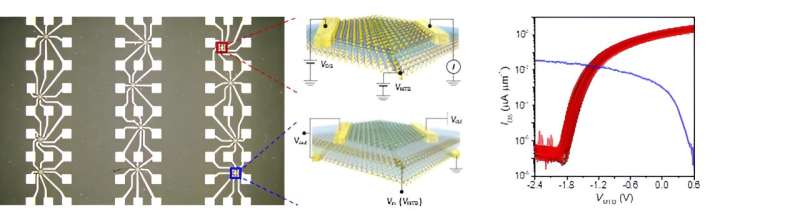
To resolve this technical downside, the analysis crew leveraged the truth that the mirror twin boundary (MTB) of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), a 2D semiconductor, is a 1D steel with a width of solely 0.4 nm. They used this as a gate electrode to beat the constraints of the lithography course of.
On this research, the 1D MTB metallic section was achieved by controlling the crystal construction of the present 2D semiconductor on the atomic stage, reworking it right into a 1D MTB. This represents a major breakthrough not just for next-generation semiconductor know-how but in addition for fundamental supplies science, because it demonstrates the large-area synthesis of recent materials phases by synthetic management of crystal buildings.
The Worldwide Roadmap for Units and Methods (IRDS) by the IEEE predicts semiconductor node know-how to succeed in round 0.5 nm by 2037, with transistor gate lengths of 12 nm. The analysis crew demonstrated that the channel width modulated by the electrical subject utilized from the 1D MTB gate will be as small as 3.9 nm, considerably exceeding the futuristic prediction.
The 1D MTB-based transistor developed by the analysis crew additionally presents benefits in circuit efficiency. Applied sciences like FinFET or Gate-All-Round, adopted for the miniaturization of silicon semiconductor gadgets, undergo from parasitic capacitance as a consequence of their advanced gadget buildings, resulting in instability in extremely built-in circuits. In distinction, the 1D MTB-based transistor can reduce parasitic capacitance as a consequence of its easy construction and intensely slim gate width.
Director Jo Moon-Ho commented, “The 1D metallic phase achieved through epitaxial growth is a new material process that can be applied to ultra-miniaturized semiconductor processes. It is expected to become a key technology for developing various low-power, high-performance electronic devices in the future.”
Extra info:
Built-in 1D epitaxial mirror twin boundaries for ultra-scaled 2D MoS2 field-effect transistors, Nature Nanotechnology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01706-1
Supplied by
Institute for Fundamental Science
Quotation:
Scientists uncover solution to ‘develop’ sub-nanometer sized transistors (2024, July 3)
retrieved 3 July 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-07-scientists-nanometer-sized-transistors.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

