Researchers from Tohoku College and Kyoto College have efficiently developed a DNA-based molecular controller that autonomously directs the meeting and disassembly of molecular robots. This pioneering know-how marks a big step in the direction of superior autonomous molecular programs with potential functions in drugs and nanotechnology.
Particulars of the breakthrough have been printed within the journal Science Advances on Could 31, 2024.
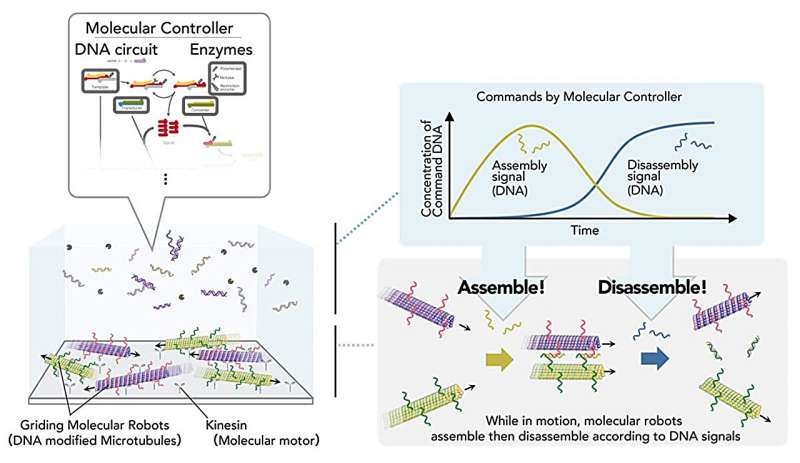
“Our newly developed molecular controller, composed of artificially designed DNA molecules and enzymes, coexists with molecular robots and controls them by outputting specific DNA molecules,” factors out Shin-ichiro M. Nomura, an affiliate professor at Tohoku College’s Graduate College of Engineering and co-author of the examine.
“This allows the molecular robots to self-assemble and disassemble automatically, without the need for external manipulation.”
Such autonomous operation is an important development, because it allows the molecular robots to carry out duties in environments the place exterior alerts can not attain.
Along with Nomura, the analysis staff included Ibuki Kawamata (an affiliate professor at Kyoto College’s Graduate College of Science), Kohei Nishiyama (a graduate scholar at Johannes Gutenberg College Mainz), and Akira Kakugo (a professor at Kyoto College’s Graduate College of Science).
Analysis on molecular robots, that are designed to help in illness therapy and prognosis by functioning each inside and outdoors the physique, is gaining important consideration.
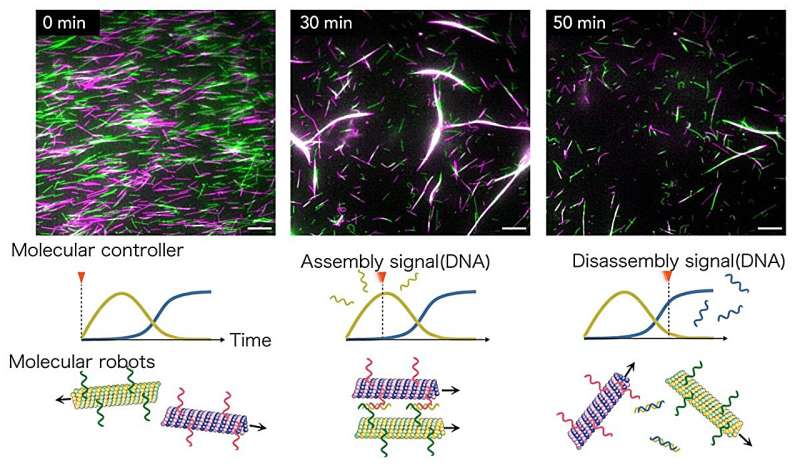
Earlier analysis by Kakugo and colleagues had developed swarm-type molecular robots that transfer individually. These robots may very well be assembled and disassembled as a gaggle by way of exterior manipulation. However because of the constructed molecular controller, the robots can self-assemble and disassemble based on a programmed sequence.
The molecular controller initiates the method by outputting a selected DNA sign equal to the “assemble” command. The microtubules in the identical resolution, modified with DNA and propelled by kinesin molecular motors, obtain the DNA sign, align their motion path, and routinely assemble right into a bundled construction. Subsequently, the controller outputs a “disassemble” sign, inflicting the microtubule bundles to disassemble routinely.
This dynamic change was achieved by way of exact management by the molecular circuit, which features like a extremely subtle sign processor. Furthermore, the molecular controller coexists with molecular robots, eliminating the necessity for exterior manipulation.
Advancing this know-how is anticipated to contribute to the event of extra complicated and superior autonomous molecular programs.
Consequently, molecular robots may carry out duties that can not be achieved alone by assembling based on instructions after which dispersing to discover targets. Moreover, this analysis expanded the exercise circumstances of molecular robots by integrating totally different molecular teams, such because the DNA circuit system and the motor protein working system.
“By developing the molecular controller and combining it with increasingly sophisticated and precise DNA circuits, molecular information amplification devices, and biomolecular design technologies, we expect swarm molecular robots to process a more diverse range of biomolecular information automatically,” provides Nomura.
“This advancement may lead to the realization of innovative technologies in nanotechnology and the medical field, such as nanomachines for in-situ molecular recognition and diagnosis or smart drug delivery systems.”
Extra info:
Ibuki Kawamata et al, Autonomous meeting and disassembly of gliding molecular robots regulated by a DNA-based molecular controller, Science Advances (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adn4490
Supplied by
Tohoku College
Quotation:
Self-assembling and disassembling swarm molecular robots by way of DNA molecular controller (2024, June 14)
retrieved 14 June 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-06-disassembling-swarm-molecular-robots-dna.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.

