Growing antiviral therapeutics and vaccines requires shut research of the viruses that trigger illness. However how can these small germs be remoted from complicated organic samples like saliva?
Researchers of a research showing in ACS Nano describe a platform that makes use of sound waves as acoustic tweezers to kind viruses from different compounds in a liquid. In demonstrations, the strategy shortly and precisely separates viruses from giant and small particles in human saliva samples.
Isolating, figuring out and genetically sequencing a virus offers essential info to scientists about the way it causes illness and how you can develop efficient therapeutics. Present strategies for separating viruses from different particles in organic samples embrace time-consuming ultracentrifugation and cell tradition procedures.
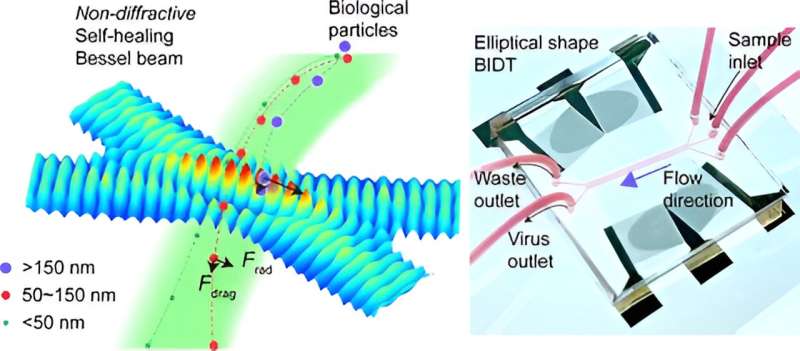
To hurry up and simplify the method, Luke Lee and Tony Jun Huang appeared to acoustofluidics: a know-how that makes use of sound waves to kind particles by measurement in a liquid. They selected a particular sort of sound wave, referred to as a Bessel beam, as a result of it may be tuned to kind particular nanosized particles, and a number of waves stay tightly targeted over lengthy distances—like a pair of tweezers.
The Bessel beam excitation separation know-how (BEST) platform that Lee, Huang and colleagues developed consists of an oblong chip with a sample-loading inlet at one finish and separate virus and waste shops on the different finish. Two acoustic Bessel beams have been utilized throughout the chip, perpendicular to the pattern move. By tuning the beams’ wavelengths, the system sorted particles of various sizes:
- Massive particles bigger than 150 nanometers (nm) in diameter have been trapped on the chip.
- Small particles smaller than 50 nm left via the waste outlet.
- Viruses of intermediate sizes (50 to 150 nm) have been collected through the virus outlet.
The staff examined the BEST platform on human saliva samples loaded with SARS-CoV-2. Liquid collected from the chip’s virus outlet contained 90% of viral genetic materials, whereas liquid from the waste outlet contained no viral genetic materials, displaying that the platform efficiently remoted the virus. The researchers confirmed the outcomes with electron microscopy, discovering viruses solely in liquid sampled from the virus outlet.
Though BEST can’t but separate waste particles from viruses which are smaller than 50 nm, reminiscent of parvoviruses, the researchers are working to broaden the know-how’s vary to allow its use in creating new therapeutic targets for quite a few viral ailments.
Extra info:
Jianping Xia et al, Acoustofluidic Virus Isolation through Bessel Beam Excitation Separation Know-how, ACS Nano (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.4c09692
Offered by
American Chemical Society
Quotation:
Separating viruses from saliva with sound waves for therapeutic research (2024, September 9)
retrieved 9 September 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-09-viruses-saliva-therapeutic.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.

