Distributed providers have certainly revolutionized the design and deployment of purposes within the trendy world of cloud-native structure: flexibility, scalability, and resilience are supplied by these autonomous, loosely coupled providers. This additionally signifies that providers add complexity to our techniques, particularly with cross-cutting issues corresponding to logging, monitoring, safety, and configuration. As a elementary design idea, the sidecar sample enhances the distributed structure in a seamless and scalable method.
All through this text, we discover what the sidecar sample affords, its use instances, and why it has develop into so extensively utilized in cloud-native environments.
What Is the Sidecar Sample?
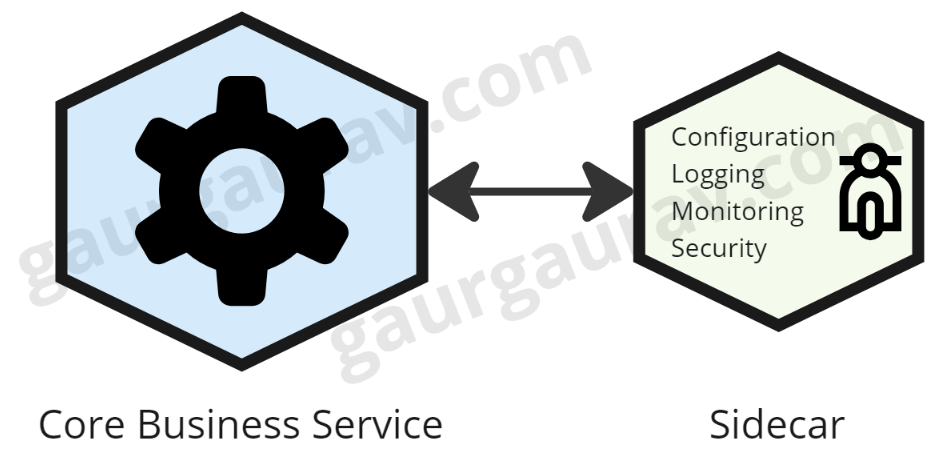
The sidecar sample describes a design that deploys an auxiliary service — a sidecar — alongside the container of a major software. It might run in its personal container or course of however would share the identical context with the first software, corresponding to community and storage. The target right here is to dump non-core enterprise logic performance — safety, logging, or configuration — to this auxiliary container and let the first service give attention to the core software logic.
Consider it as attaching a sidecar to a motorbike. The bike is your app, and the sidecar supplies help with out getting in the best way of the bike’s operation.
Why Use the Sidecar Sample?
The sidecar sample offloads non-core functionalities corresponding to authentication, logging, or configuration right into a separate element. That may make sure that your predominant service has just one concern: enterprise logic; thus, will probably be simpler to keep up and check.
Furthermore, sidecars don’t rely upon the principle software’s language or expertise stack. This enables one to standardize issues throughout a number of providers written in any language. As soon as a sidecar has been written, it may be reused throughout many providers, which ensures its functionalities would stay constant. For example, a logging sidecar utilized to a number of microservices would end in widespread log formatting and supply.
Since these sidecars can handle logging, tracing, or metrics gathering fairly independently, they are going to certainly present a clear method to inject observability into the providers with out touching their enterprise logic. This grants far more visibility and higher troubleshooting. Lastly, this replace within the logic of a sidecar-such as upgrading a safety feature-doesn’t must make modifications to the principle software. This supplies higher agility whereas decreasing downtime, no less than in massive distributed techniques. Thus, sidecars permit attaining:
- Separation of issues
- Modular and reusable parts
- Improved observability
- Permits simpler service updates
Key Use Circumstances for the Sidecar Sample
Service Meshes
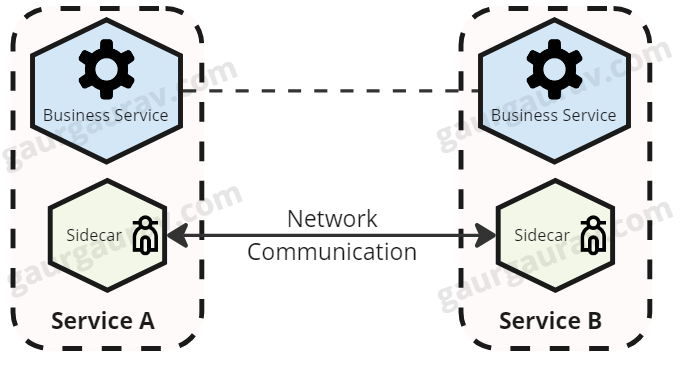
Probably the most well-known usages of the sidecar sample is service meshes, corresponding to Istio or Linkerd. The sidecar proxy (Envoy, for instance) manages networking issues corresponding to routing, load balancing, retries, and even safety between providers — for instance, mutual TLS. The sidecar supplies a clear layer of management with out altering software code.
Safety Enhancements
Varied safety insurance policies may very well be applied through sidecars, together with secret administration, certificates rotation, or knowledge encryption. As a particular instance, mutual authentication between providers will be dealt with by a sidecar, maintaining delicate knowledge transmissions safe.
Monitoring and Logging
Centralized logging can run in sidecar containers, corresponding to Fluentd or Logstash, which acquire and ahead logs to a central server, abstracting log administration from the applying. Equally, a monitoring sidecar exposes an software’s metrics to a monitoring system like Prometheus.
Configuration Administration
One of many use instances for sidecars is to dynamically load and inject configuration knowledge into the principle software. That is helpful when configurations want to alter at runtime and with out restarting the principle service.
Issues To Contemplate When Utilizing Sidecar Sample
Whereas the sidecar sample enjoys a number of benefits, it is equally vital to concentrate on what trade-offs it makes:
- Useful resource overhead: Sidecars eat CPU, reminiscence, and networking assets. A number of sidecars performing completely different duties, corresponding to logging or monitoring, will enhance useful resource consumption.
- Operational complexity: Operating sidecars for a lot of providers is an operational activity and a problem. Very similar to the principle providers, sidecars should be appropriately deployed, up to date, and monitored.
- Community latency: Since a lot of the sidecars work together over the community, proxy sidecars, as an example, might introduce further community latency. Usually negligible, however an vital consideration the place efficiency is delicate.
Greatest Practices Making use of the Sidecar Sample
- Sidecars share the identical assets as the principle container, it’s good follow to maintain sidecar processes light-weight to cut back rivalry on assets.
- Set up sidecars for cross-cutting issues like logging, safety, and configuration. Core enterprise logic shouldn’t go into the sidecar since this may trigger tight coupling between the applying and the sidecar.
- Like software providers, monitor the useful resource consumption of your sidecars, for instance failure charges and efficiency degradations.
- If utilizing service mesh applied sciences that rely upon sidecars, make sure that the advantages introduced by sidecar injection, corresponding to observability and safety, justify the elevated operational complexity.
Conclusion
Offloading cross-cutting issues to sidecars creates extra modular, reusable, and maintainable providers. As with all sample of structure, one must steadiness advantages towards potential overhead and the extent of complexity it introduces. Used appropriately, the sidecar can vastly simplify distributed structure whereas retaining flexibility and scalability.
Because the cloud-native structure continues to evolve, the sidecar sample will undoubtedly stay an vital technique for coping with the growing complexity of distributed techniques.

