A world crew of scientists, together with two researchers who now work within the Heart for Superior Sensor Know-how (CAST) at UMBC, has proven that twisted carbon nanotubes can retailer thrice extra vitality per unit mass than superior lithium-ion batteries. The discovering could advance carbon nanotubes as a promising answer for storing vitality in units that have to be light-weight, compact, and protected, akin to medical implants and sensors. The analysis was revealed lately within the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
Sanjeev Kumar Ujjain, from CAST, was a lead researcher on the work. He began the challenge whereas at Shinshu College, in Nagano, Japan, and continued after arriving at UMBC in 2022. Preety Ahuja, from CAST, additionally contributed to the fabric characterization features of the analysis.
The researchers studied single-walled carbon nanotubes, that are like straws constituted of pure carbon sheets solely 1-atom thick. Carbon nanotubes are light-weight, comparatively straightforward to fabricate, and about 100 instances stronger than metal. Their wonderful properties have led scientists to discover their potential use in a variety of futuristic-sounding know-how, together with house elevators.
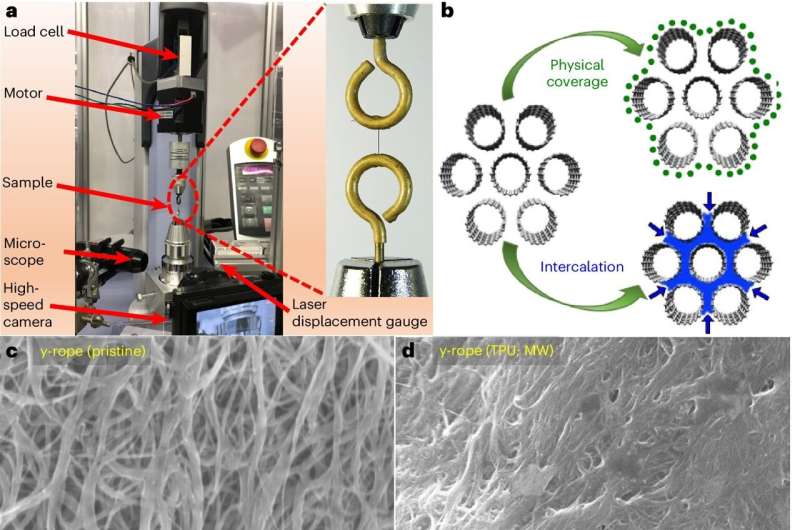
To analyze carbon nanotubes’ potential for storing vitality, the UMBC researchers and their colleagues manufactured carbon nanotube “ropes” from bundles of commercially accessible nanotubes. After pulling and twisting the tubes right into a single thread, the researchers then coated them with totally different substances supposed to extend the ropes’ energy and adaptability.
The crew examined how a lot vitality the ropes might retailer by twisting them up and measuring the vitality that was launched because the ropes unwound. They discovered that the best-performing ropes might retailer 15,000 instances extra vitality per unit mass than metal springs, and about thrice extra vitality than lithium-ion batteries.
The saved vitality stays constant and accessible at temperatures starting from -76 to +212 °F (-60 to +100 °C). The supplies within the carbon nanotube ropes are additionally safer for the human physique than these utilized in batteries.
“Humans have long stored energy in mechanical coil springs to power devices such as watches and toys,” Kumar Ujjain says. “This research shows twisted carbon nanotubes have great potential for mechanical energy storage, and we are excited to share the news with the world.”
He says the CAST crew is already working to include twisted carbon nanotubes as an vitality supply for a prototype sensor they’re growing.
Extra info:
Shigenori Utsumi et al, Large nanomechanical vitality storage capability in twisted single-walled carbon nanotube ropes, Nature Nanotechnology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01645-x
Supplied by
College of Maryland Baltimore County
Quotation:
Twisted carbon nanotubes might obtain considerably higher vitality storage than superior lithium-ion batteries (2024, July 26)
retrieved 26 July 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-07-carbon-nanotubes-significantly-energy-storage.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

