Nationwide College of Singapore (NUS) chemists have developed a technique utilizing disulfide-containing small molecules to facilitate the reversible management and supply of ribonucleic acid (RNA).
RNA-based therapeutics have emerged as one of the crucial sought-after therapeutic modalities in recent times. Nonetheless, RNA supply stays a serious problem within the discipline. Lipid nanoparticles, regardless of being broadly used for RNA supply together with the supply of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, face a number of limitations similar to their effectiveness and security. Various strategies that may probably overcome these limitations are extremely fascinating.
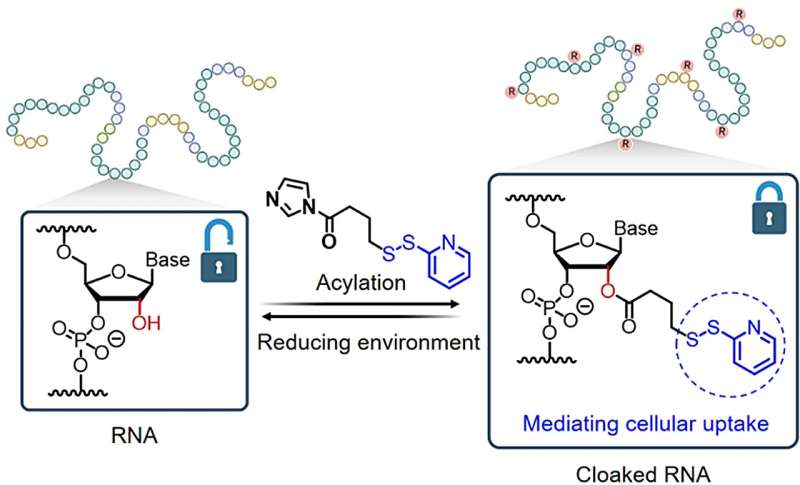
A analysis staff led by Assistant Professor Zhu Ru-Yi, from the Division of Chemistry at NUS have developed a way that takes benefit of a chemical course of known as post-synthetic RNA acylation chemistry, and mixed it with dynamic disulfide trade response for RNA supply and reversible management. The analysis findings are printed within the journal Angewandte Chemie Worldwide Version.
This technique gives a option to masks the RNA molecule, and researchers can probably regulate its exercise and supply till it reaches its goal web site inside the cell.
The researchers discovered that by including particular chemical markers (disulfide-containing teams) to the RNA, these teams can block RNA’s catalytic exercise and folding, quickly hiding the directions. Then, when wanted, they’ll activate the RNA by eradicating these markers, permitting cells to learn and act upon the directions once more.
This technique permits the RNA to enter cells rapidly, distribute successfully, and turn out to be energetic within the cell’s cytosol with out getting trapped in lysosomes. The researchers imagine that their methodology will likely be accessible to laboratories engaged in RNA biology and holds promise as a flexible platform for RNA-based purposes.
Prof Zhu stated, “Our studies showcase the first example of RNA delivery into cells using only small molecules.”
“The simplicity of our method for modifying RNA and the unique delivery mechanism will undoubtedly attract more researchers to adopt and improve the method. We believe that our work will facilitate numerous applications in the field of RNA biology and biomedicines,” added Prof Zhu.
Wanting forward, the analysis staff is actively designing new methods to switch RNA and enhance RNA-based therapeutics.
Extra data:
Junsong Guo et al, RNA Management by way of Redox‐Responsive Acylation, Angewandte Chemie Worldwide Version (2024). DOI: 10.1002/anie.202402178
Supplied by
Nationwide College of Singapore
Quotation:
Unlocking RNA performance: A redox-responsive method (2024, June 6)
retrieved 7 June 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-06-rna-functionality-redox-responsive-approach.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.

