Analysis teams from the College of Tsukuba and the College of Rennes have found a novel phenomenon through which a nested construction of carbon nanotubes enveloped in boron nitride nanotubes facilitates a novel electron escape route when uncovered to mild. This discovering introduces promising avenues for numerous purposes, together with the creation of high-speed optical units, fast management of electrons and different particles and environment friendly warmth dissipation from units.
Latest research have highlighted that supplies composed of layered tubes, that are atomically thick and categorized as low-dimensional supplies, exhibit new properties. Though the static properties of those constructions, corresponding to electrical conduction, are nicely documented, their dynamic properties, together with electron switch between layers and atomic movement triggered by mild publicity, have obtained much less consideration.
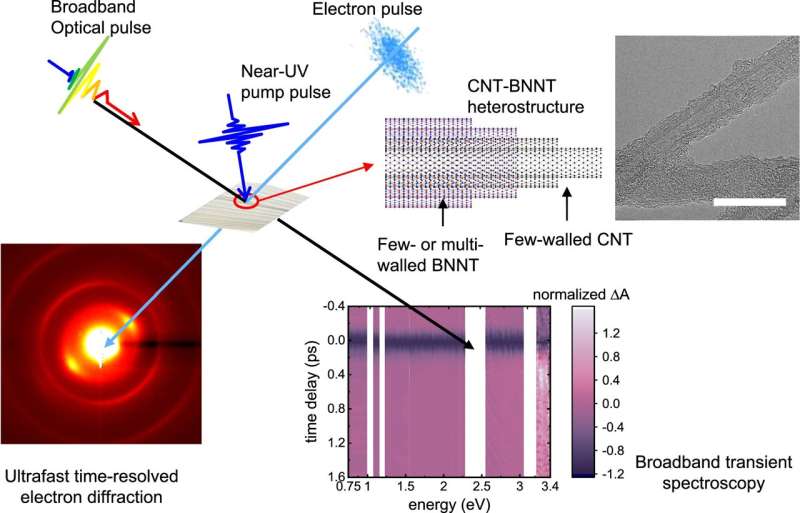
On this examine, researchers constructed nested cylindrical constructions by wrapping carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in boron nitride nanotubes. They then examined the movement of electrons and atoms induced by ultrashort mild pulses on a one-dimensional (1D) materials. The examine is revealed within the journal Nature Communications.
Electron movement was monitored utilizing broadband ultrafast optical spectroscopy, which captures instantaneous adjustments in molecular and digital constructions as a result of mild irradiation with a precision of ten trillionths of a second (10−13 s). Atomic movement was noticed by means of ultrafast time-resolved electron diffraction, which equally achieved monitoring of structural dynamics with ten-trillionth-of-a-second accuracy.
The examine revealed that when various kinds of low-dimensional supplies are layered, a pathway or channel varieties, permitting electrons to flee from particular subparts of the fabric. Moreover, it was discovered that electrons excited within the CNTs by mild publicity may switch into the BNNTs through these digital channels, the place their vitality is quickly transformed into thermal vitality, facilitating extraordinarily quick thermal conversion.
This analysis has uncovered a brand new bodily phenomenon on the interface between two dissimilar supplies, providing not solely ultrafast thermal vitality transport but additionally potential purposes within the improvement of ultrafast optical units and the fast manipulation of electrons and holes generated by mild.
Extra info:
Yuri Saida et al, Photoinduced dynamics throughout digital switch from slender to large bandgap layers in one-dimensional heterostructured supplies, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-48880-3
Offered by
College of Tsukuba
Quotation:
Unveiling novel vitality phenomena from mild publicity on layered supplies (2024, June 7)
retrieved 7 June 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-06-unveiling-energy-phenomena-exposure-layered.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

